Empowering Financial Compliance: Data-Driven Approach in AML Compliance with Roche Pretorius
Executive Summary
This webinar covers a conversation by Roche Pretorius demonstrating RAHN with a focus on data and anti-money laundering, focusing on challenges in data integration and risk mitigation. Roche includes an introduction to compliance tools, challenges faced by tools for identifying implicated individuals and entities, and key features of a comprehensive data set. Additionally, the webinar touches upon the use of AI in data analytics tools, custom algorithm and tool capabilities, organization and functionality of the dashboard, monitor GPT and report generation.
Webinar Details
Title: Empowering Financial Compliance: Data-Driven Approach in AML Compliance
URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hbpfC0SUzM0
Date: 27 February 2024
Presenter: Roche Pretorius
Meetup Group: DAMA SA User Group
Write-up Author: Howard Diesel
Contents
Business Conversation on Data and Anti-Money Laundering
Challenges in Data Integration and Risk Mitigation
Introduction to Compliance Tool
Challenges Faced by Tools for Identifying Implicated Individuals and Entities
Key Features of Our Tool
Advanced AI Due Diligence
Integration and Custom Database Features
Features of a Comprehensive Data Set
Data Sourcing and Consolidation
Data Sourcing and Management
Data Management and Schema Structure
Data Management and Security in Data Story Solutions
Website Data Management Capabilities
Data Management Technical Specifications and Compliance
System Performance and GDPR Compliance
Comprehensive Data Management Approach
Implementation of AI in Data Analytics Tools
Technology Mix and Decision-Making
Custom Algorithm and Tool Capabilities
Organisation and Functionality of Dashboard
Monitor GPT and Report Generation
Integration of Monitor GP2 and Data Duplication
Organisation and Functionality of the Custom Database and Adverse Media
AI and Data Monitoring
Overview of Investigative Tooling Features
Evolution of Data Analysis
Discussion on Financial Risk Management
Risk Mitigation and Compliance Plan
Business Conversation on Data and Anti-Money Laundering
Roche Pretorius express gratitude for the opportunity to showcase their work on anti-money laundering, highlighting that RAHN started as a data problem and eventually led to the tool they supply for anti-money laundering. Roche shares that the webinar will focus on implementing an anti-money laundering end system for a South Africa-listed entity, addressing the need to meet deadlines and working with big SA companies.
Figure 1 RAHN: Focused, Innovative and Effective
Challenges in Data Integration and Risk Mitigation
The data integration process proved challenging, as it did not align with the promises made by the salesman, leading to complexities in integrating the data with existing systems. Building algorithms to understand the integrated data proved to be time-consuming and complex. Roche notes that the team developed methodologies to solve problems and prioritised risk by analysing potential risks from 60,000 individuals, narrowing it down to the five highest risks.
The inability to change, add, or adapt anything priced in Dollars or Euros led to the creation of MonRon. The size of penalties and financial risk varies depending on the regulator, company size, and severity of breach or non-compliance, making it a difficult question to answer.
Figure 2 Webinar Agenda
Introduction to Compliance Tool
RAHN is a comprehensive platform designed to help companies manage associated risks related to screening obligations for politically exposed individuals, sanctions, and adverse media. It includes core functions such as data sourcing and management, automation, data storage, compliance measures, and system performance.
The fine for non-compliance is significant, but there is also a broader responsibility for corporate citizenship in solving societal problems. The tool is publicised and available, substantially impacting companies and requiring dedicated teams to manage the associated risks. Its focus is on risk management and tolerance levels.
Figure 3 Introduction to Rahn Monitor
Challenges Faced by Tools for Identifying Implicated Individuals and Entities
Identifying implicated individuals and entities can be an expensive and complex task due to the use of house-developed tools that rely on massive amounts of manual research. Using fuzzy logic can lead to black box scenarios and difficulty prioritising risks, while integration with these tools can be complex, and scalability issues can arise. The emphasis on rules-based systems limits the adaptability of the tools, and many are black box in nature, requiring specialists for any changes to the risk rating, often involving remote access to systems.
Key Features of Our Tool
Roche notes that RAHN is a locally developed solution that provides streamlined algorithms for case management and allows for multiple integration points and cloud-based scalability. It has artificial intelligence built-in for enhanced functionality and a daily updated database with approximately 3.5 million individuals and entities. The tool is estimated to expand to 75 million and was created with cost mitigation in mind. It is a valuable solution for solving remote access to systems.
Advanced AI Due Diligence
The goal is to reach 75 million individuals, and AI is used for due diligence to identify potentially risky individuals. The list is narrowed down and analysed using AI reporting capabilities with a probability-matching algorithm. Roche shares that reports can be generated in Excel and PDF formats and the platform is seamlessly processed online, with integration points including badge notification and continuous monitoring. The continuous monitoring option allows notifications of individuals added to the sanctions list, and users can switch on or off notifications based on permissions and preferences.
Figure 4 Core Functions of Rahn Monitor
Integration and Custom Database Features
This tool offers seamless integration through APIs, enabling real-time feeds and outputs that significantly reduce the onboarding process. The custom database feature allows organisations to import a list of "do not do business with" individuals for scanning and identification. Additionally, it helps find a single version of the truth in client data by matching and integrating multiple data sets into a central repository.
The custom database achieves this by using the same methodology as the sanctions list for matching client and source data while assessing probability. Lastly, the tool provides global sanction coverage, making it a comprehensive solution for organisations.
Features of a Comprehensive Data Set
RAHN offers access to comprehensive data sets for informed due diligence, downloadable search results, daily updates, and an adverse media site for further investigation and risk identification. With over 2,000 new sources and proprietary GPT natural language processing capability, it enables case management and narrowing down risky individuals based on probability.
The tool offers real-time, up-to-date data enrichment and immediate availability of information. It also uses Master Data matching and entity resolution techniques for finding duplicates and matching features and has expanded its capability to include GPT natural language processing for matching. An example of identifying a risky individual in a newspaper article showcases its effectiveness.
Data Sourcing and Consolidation
This approach uses an algorithm with a specific pattern to identify patterns and improve through continuous learning and improvement. Its goal is to obtain a golden record of customer data and build Master Data from it, helping to resolve customer duplicates by comparing a source and target and configuring the output accordingly.
Data sourcing involves handling 20 gigs of data daily, including XML files from sanctions organisations that contain comprehensive information about individuals, including names, nationalities, addresses, and ID numbers. The process combines large data sets from various sources that may need to be scraped for information, including HTML, PDF, and web pages.
Figure 5 Data Sourcing and Consolidation
Data Sourcing and Management
Roche notes that the data set consists of public information, such as names, addresses, and ID numbers, with limited information available. The accuracy of the data set may be affected by gaps and inconsistencies due to legacy systems and acquisitions, requiring consolidation and validation.
Specialised sources like Interpol and SAPS are unified into a standardised database or data table through website scraping while complying with legal requirements. Regular monitoring and updating of scraping tools are necessary to ensure legal compliance and functionality as website structures change, along with continuous adherence to ethical and legal standards.
Data Management and Schema Structure
Roche notes that RAHN manages roughly 20 gigabytes of data through a structured schema, including Metadata tables for transparency and indexing for performance. The primary entity table is supported by relationship, audit, and history tables, ensuring adherence to standards, compliance, and security. Daily automation through GitHub handles large data volumes with versioning and backup options. Scheduled updates run daily at midnight to add, remove, and update records, and the organisation boasts readily available skill sets to maintain this efficient environment.
Figure 6 Database Management and Schema
Figure 7 Automation with GitHub Actions and Windows Server 2023
Data Management and Security in Data Story Solutions
The system is designed to handle up to 5 million records and is built for high-volume processing, including scraping jobs, XML jobs, and PDFs. Daily updates run for 30 minutes to an hour for three and a half million records over 1150 lists. Data is stored in the Microsoft cloud, with client data separated from internal data in SQL services to ensure privacy and security. Raw data files can be uploaded in CSV format for bulk processing, and batch and API processing is done in memory for purging and cleaning after processing.
Figure 8 Data Storage Solutions
Website Data Management Capabilities
Roche covers the key aspects of performance metrics, monitoring, API and batch handling, object-relational mapping with Prisma, streamlining of operations, batch screening, single search functions, service levels, CRM integration, and client interaction. He includes details on uptime, processing time, data integrity, resource utilisation, and insert, delete, and update operations. Monitoring for downtime and notifications for availability are also included.
The API and batch handling features meet security and compliance requirements. Prisma's object-relational mapping simplifies data creation, reading, updating, and deleting. Streamlining of operations and integration into the data model is also covered. The batch screening and single search functions are based on organisation volume, and different service levels are offered based on organisation type and volume. CRM integration provides real-time and batch processing, as well as flexibility in data input. Roche adds that the system provides client interaction and an adaptable interface to suit varied needs.
Figure 9 CRUD Operations with Prisma ORM
Figure 10 Client Data Handling: Batch vs API
Data Management Technical Specifications and Compliance
The system is designed for efficiency, scalability, and data management, focusing on distinguishing between batch and API handling. Security and compliance measures include session state cookies, two-factor authentication, and adherence to legal standards for data protection and privacy.
Regular audits ensure proper results, updates, scalability, and performance. The system operates on a pay-as-you-go model with no additional fees other than what is used. It currently adheres to GDPR principles, but external jurisdictional and data privacy requirements are anticipated and not yet addressed due to a lack of relevant clients. Additionally, secondary users must have compliance in place for downstream processing authorisation.
Figure 11 Security and Compliance Measures
System Performance and GDPR Compliance
RAHN is currently preparing for GDPR compliance and collecting international citizens' records. Roche notes that the information used is public domain and in line with international laws and standards but shares uncertainty about how to apply international laws. The company's system performance and scalability are managed through spread operations and Prisma, and their API design is done through the Flask server and Open AI as API specifications, with over 100 API routes built into the system. The architecture is robust, adaptable, and designed for scalability.
Figure 12 System Performance and Scalability
Comprehensive Data Management Approach
Efficient and clean data management involves consolidating duplicate records and combining lists to reduce instances of repeated data. A robust data foundation is crucial for operational effectiveness, achieved by systematically sourcing and consolidating data. Advanced data handling using SQL ensures effective data processing without the need for complex methods.
Streamlined data maintenance processes prioritise data efficiency and integrity. Flexibility in data processing allows for effective integration. Security compliance is a priority, with a comprehensive authorised reference data list and a clearing option for everything in the database except for regulatory criminal listings, which cannot be opted out of.
Figure 13 Conclusion
Implementation of AI in Data Analytics Tools
Roche covers the implementation of AI in data analytics tools, the practicality of web scraping in such tools, and the importance of AI in improving services and offering value to clients. The tool allows for one-click clearing of all data, except for regulatory criminal listings. Adopting AI technology and analysing transaction patterns are areas that will be expanded in the future.
Technology Mix and Decision-Making
Roche is currently engaged in an interesting problem related to ESG sustainability. They have analysed balance sheets and moved from standardising input to using a prototype using Large Language Models (LLM). Various technologies, including Prisma or RM for the backend and Flask for the web GUI, are used based on resource availability, necessary functionality, and security and legal considerations. Roche acknowledges that historical reasons often play a role in decision-making, opting not to use a traditional Master Data system. Roche created his solution for matching and resolving data to gain more functionality and flexibility in the matching algorithm.
Custom Algorithm and Tool Capabilities
A discussion on the importance of developing problem-solving skills and flexibility highlights the importance of learning to do things independently. Roche covers the option for clients to create custom algorithms to build different scenarios for reporting and operational reality. Ensuring a unique customer identification is also emphasised, highlighting the complexity and attributes needed. The tool capabilities discussed included user login, a standard dashboard, a website with a video explaining capabilities, and a focus on name matching and unique customer key creation.
Figure 14 RAHN Monitor Website
Organisation and Functionality of Dashboard
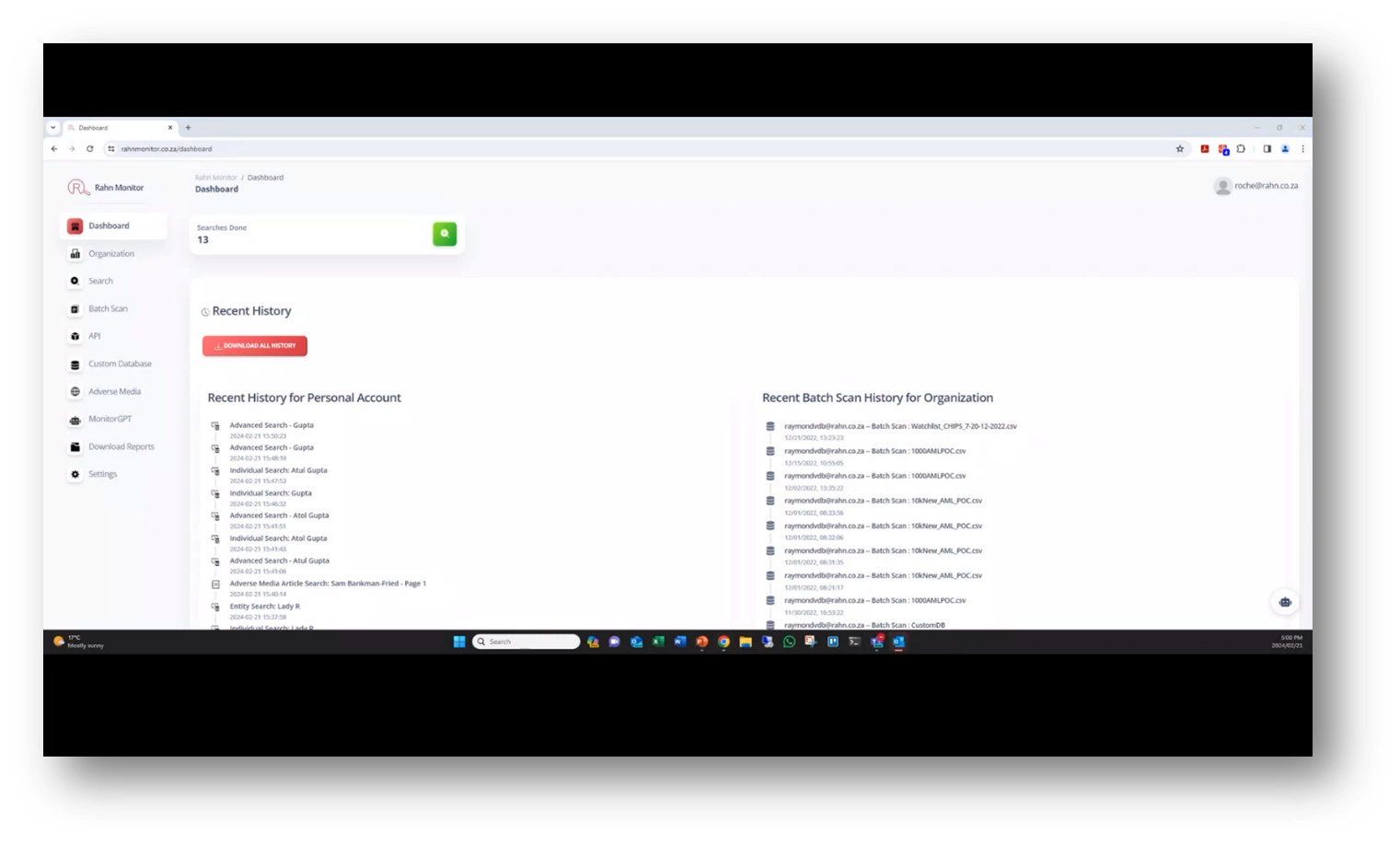
Roche notes that the compliance platform is designed to cater to multiple organisations and professionals offering compliance services to small organisations. The platform supports hierarchical multitenancy, enabling different levels of multitenancy for various clients under a user's profile.
The dashboard displays recent searches from an organisational perspective, and the search function allows users to search for specific entities or individuals, providing detailed information on their status and analysis from various lists. This feature allows compliance managers to view batch perspectives in one context and separate client data, making it a useful tool for managing compliance services.
Figure 15 Recent History
Figure 16 Create Organisation
Figure 17 Perform a Search
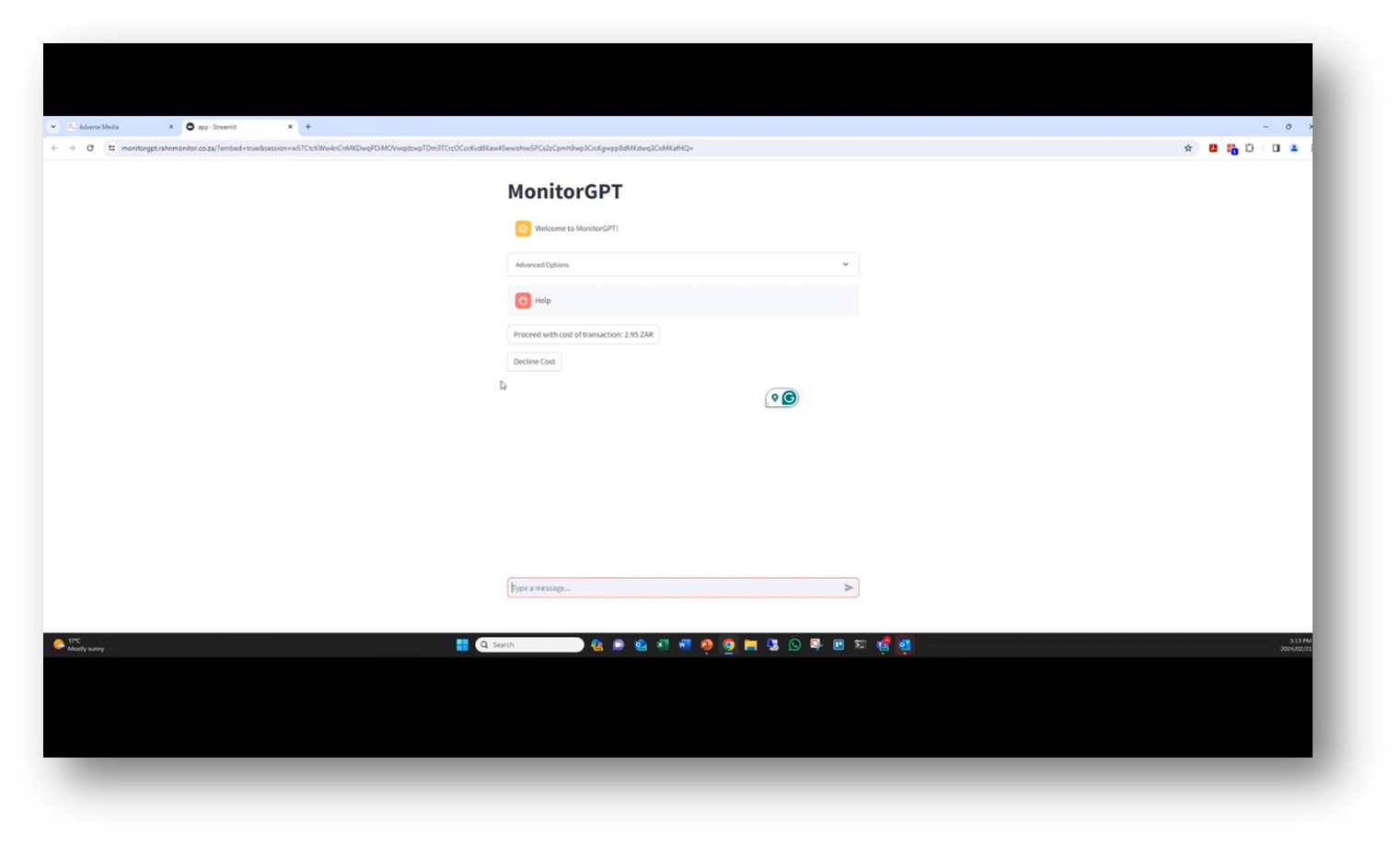
Monitor GPT and Report Generation
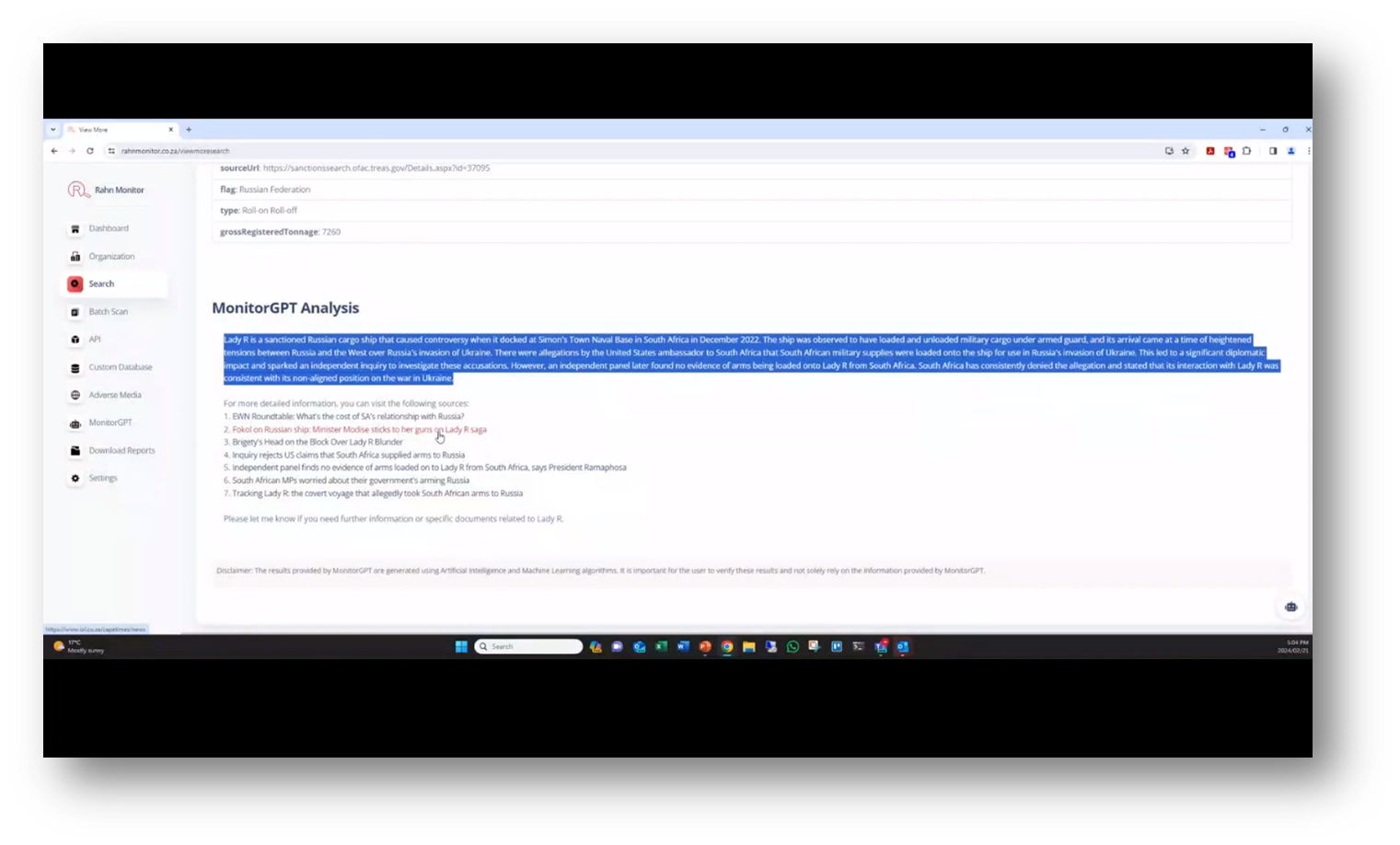
An important aspect of transparency is providing access to the links used in GPT analysis. IDs provide names, submission dates, and relevant information from sanctions lists. Reports can be generated and white-labelled for different purposes, such as for risk committees or onboarding clients. Additionally, batch scan capability enables users to upload and process data in a CSV template, minimising manual processing.
Figure 18 MonitorGPT Analysis
Integration of Monitor GP2 and Data Duplication
Roche notes that including the Monitor GP2 in the output may result in additional costs due to GP2 cost for every call made. Additionally, the API only matches based on name, full name, date of birth, and country, with the response given back containing probabilities of matching rather than a 100% match.
Matches are categorised as potential positive match, borderline match, and potentially false positive to optimise focusing on specific lists. The integration of Monitor GP2 can reveal data quality issues in the existing dataset. It is important to remember that requesting data beyond name, date of birth, and country may lead to data quality and completeness issues.
Organisation and Functionality of the Custom Database and Adverse Media
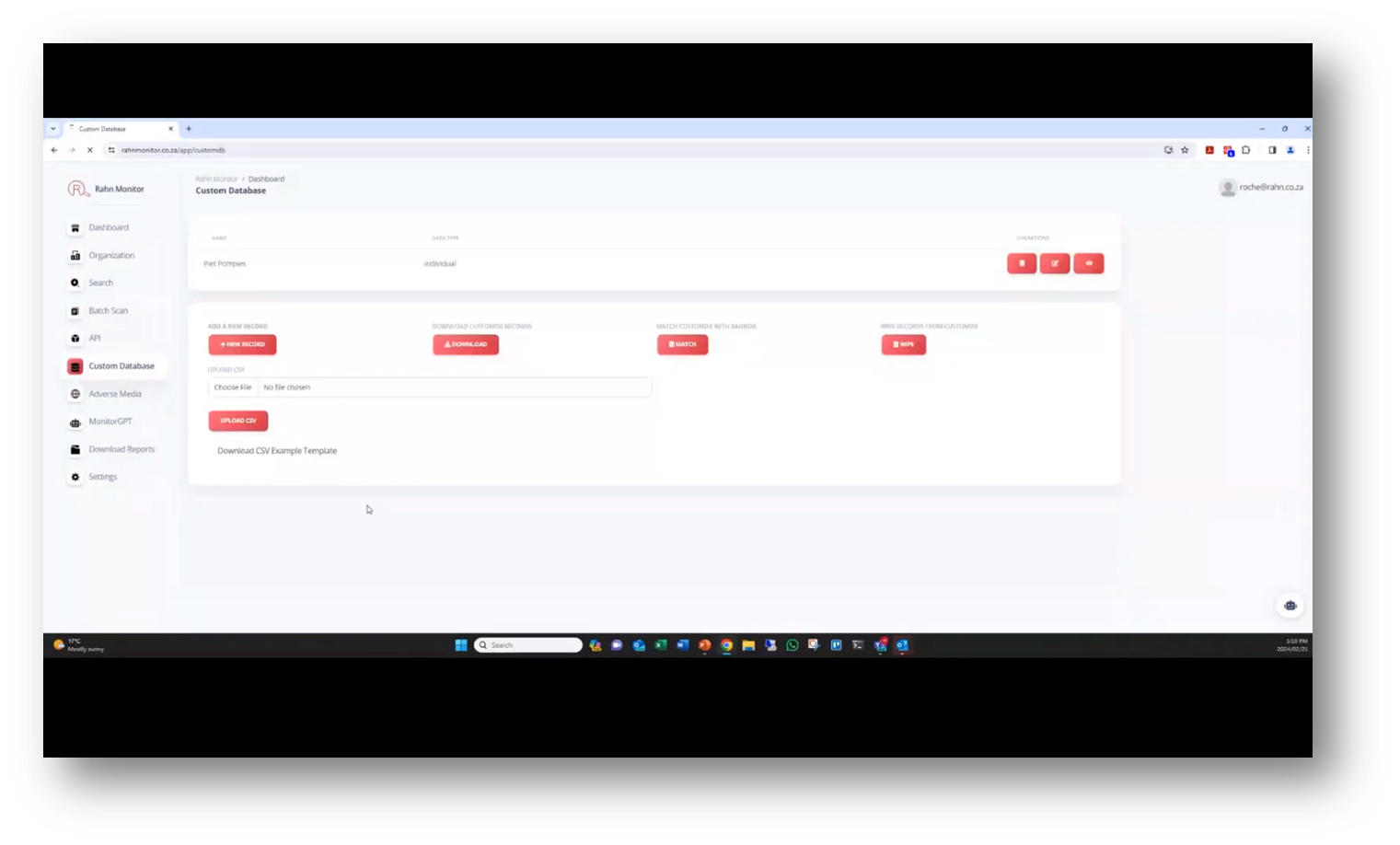
This system offers an API to generate keys and access documentation for interacting with the system. Additionally, it provides a custom database function to upload, manage and categorise lists of individuals for tracking their access to an organisation’s systems. This database offers multiple functions, such as downloading, adding, uploading, matching, and managing individual records, and can be used to identify high-value individuals or flag individuals for special treatment. The adverse media feature is divided into three sections for tracking and analysing news reports. Both the custom database and adverse media features are essential tools for monitoring and managing access to an organisation's systems.
Figure 19 Custom Database
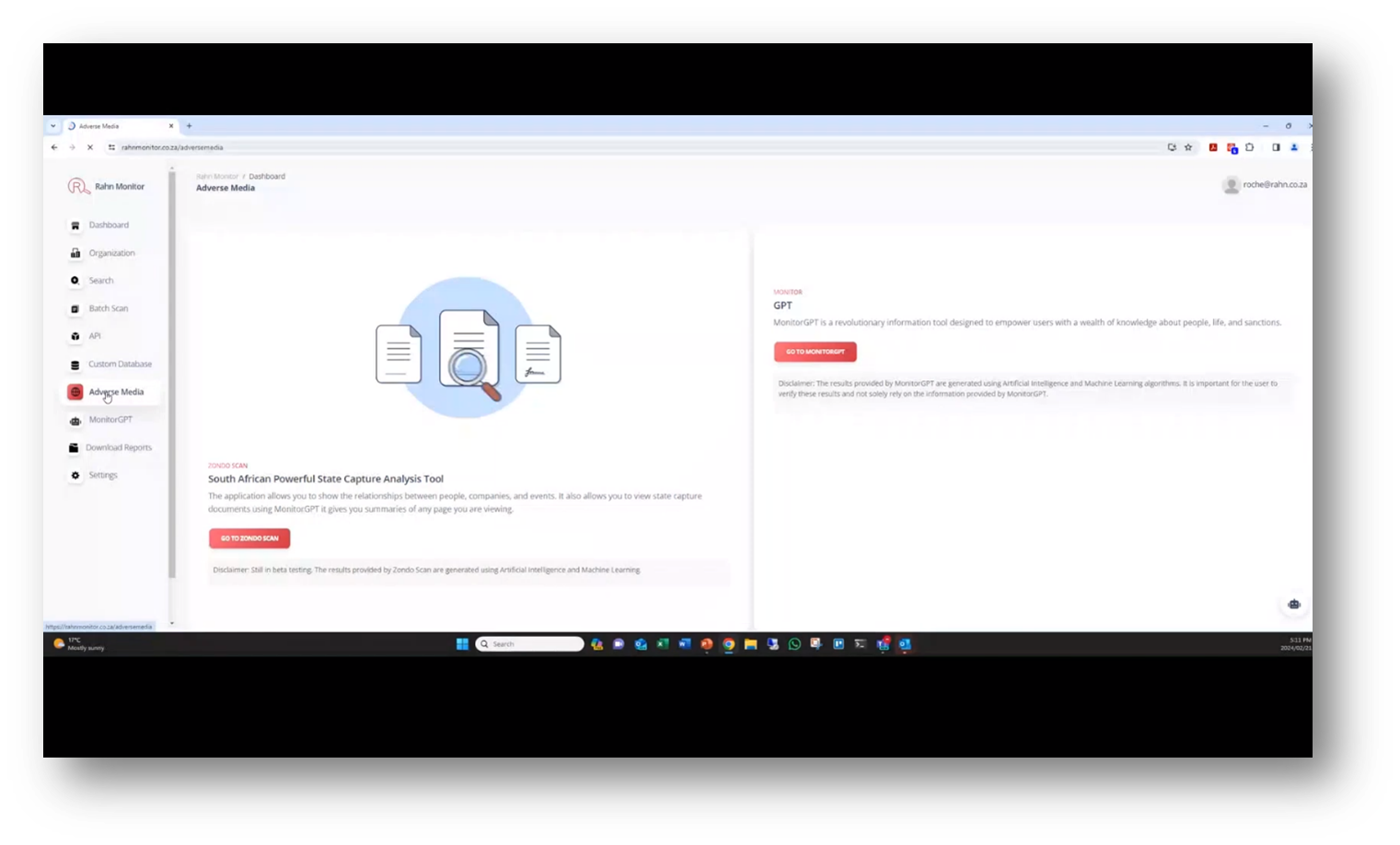
AI and Data Monitoring
The state capture report was digitised before AI technology was widely available and can be accessed for public use to check individuals against the sanctions list. Monitor GPT, a tool that uses AI for analysis and screening, includes an adverse media feature that scans 2,000 news sources for keywords associated with financial or general crime.
The tool can also use documents and previous messages for analysis and can be tailored to user needs. Its purpose is to understand better individuals, such as clients mentioned in the text, with tokenisation converted into a cost.
Figure 20 Adverse Media
Figure 21 MonitorGPT
Overview of Investigative Tooling Features
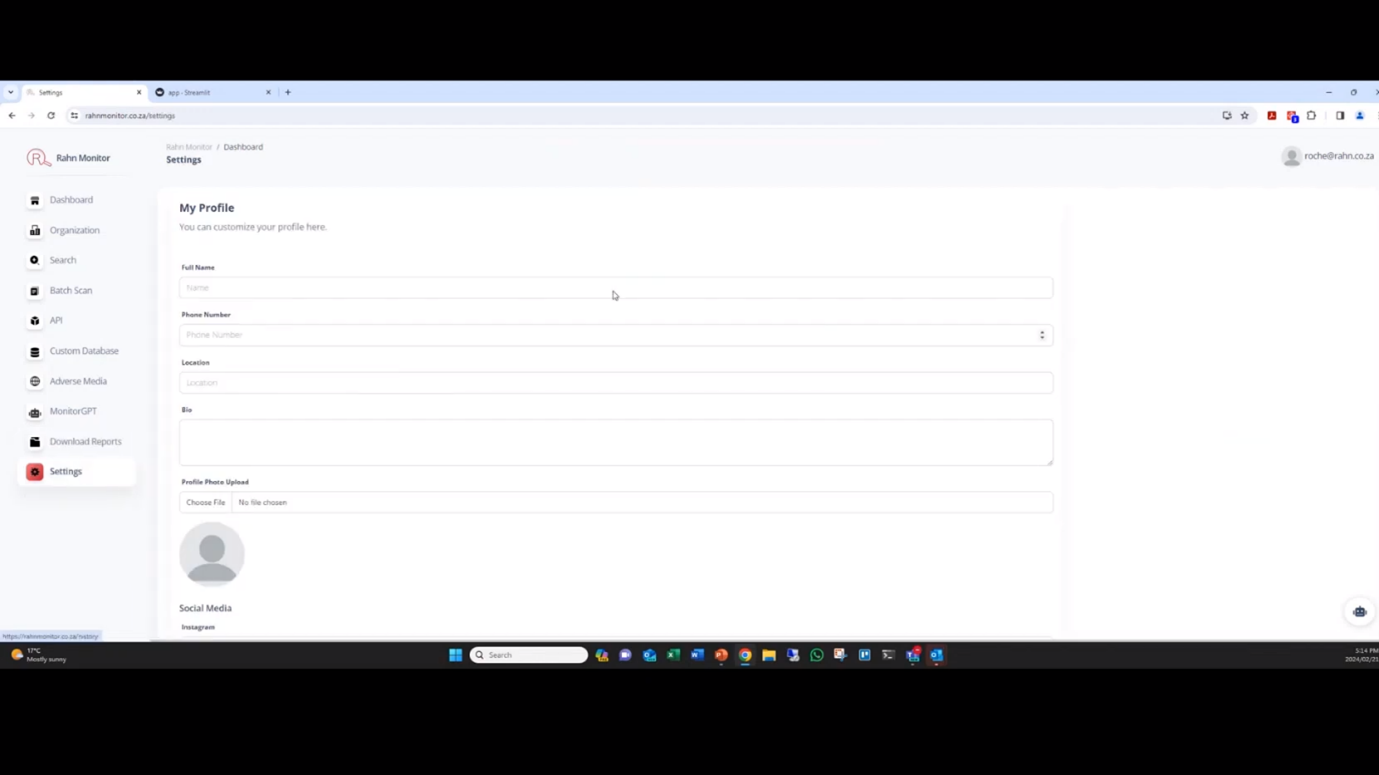
RAHN provides real-time, comprehensive information with detailed reports that can be downloaded. Roche notes that users can customise individual elements in the settings and identify low-risk individuals with the whitelist feature. Continuous monitoring notifications can be enabled to receive alerts for any changes in client data. The tool includes two-factor authentication and a one-button option to remove all information.
Figure 22 Settings: My Profile
Evolution of Data Analysis
Data analysis involves deriving probabilities of matching records using models for clients, risk dissemination, and machine learning. The process requires efficient searches that run quickly and involve much background work to gather all the necessary data. With the evolution of data analysis, the process continues to expand and grow as the team learns more about it. Despite the challenge of running one record against millions, the team does it efficiently and continuously improves.
Discussion on Financial Risk Management
Roche discusses the potential for a bad actor to cause problems with a massive customer database, emphasising the importance of regularly scanning the entire data set to ensure compliance with legislation and regulatory requirements while managing risks. He suggests establishing a baseline and monitoring the entire data set to ensure no one has bypassed the onboarding process or entered the system fraudulently. Roche also mentions that regulators are concerned with identifying and managing risks rather than dictating all the risks a company may face.
Risk Mitigation and Compliance Plan
Organisations must establish clear risk mitigation and compliance plans (RMCP) standards. The standard should consider the perceived risk and industry type, such as the difference in risk perception and mitigation between long-term insurers and banks. Hash keys and entity comparisons should be used for scanning and data quality assessment. At the same time, fuzzy logic can be implemented for matching and data remediation programs to address data quality issues. Experience with automated reporting and data quality solutions can lead to a more effective RMCP.
If you would like to join the discussion, please visit our community platform, the Data Professional Expedition.
Additionally, if you would like to be a guest speaker on a future webinar, kindly contact Debbie (social@modelwaresystems.com)
Don’t forget to join our exciting LinkedIn and Meetup data communities not to miss out!