Designing Data Products to Support Customer Value Propositions for Data Citizens
Executive Summary
This webinar covers various crucial topics including customer value proposition, data product design, business model canvas, customer identification, and entity resolution. Howard Diesel emphasises the importance of customer-centric communication, understanding customer needs and jobs, and the role of a Chief Data Officer (CDO) in achieving social gain and respect within the organisation. The webinar also highlights the significance of measuring a CDO's benefits and responsibilities and the fit of the business model. Additionally, Howard explores customer segments, double-sided platforms, network effects, and the importance of an entrepreneurial mindset in business. Lastly, he stresses the significance of reinventing the business model, researching and innovation in a business context, enterprise-level problem-solving, and measuring and data collection in business strategy.
Webinar Details
Title: Designing Data Products to support Customer Value Propositions for Data Citizens
URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6BH0IPJzKmA
Date: 24 July 2024
Presenter: Howard Diesel
Meetup Group: African Data Management Community
Write-up Author: Howard Diesel
Contents
Customer Value Proposition and Data Product Design
Value Proposition and Business Model Canvas
Business Model Canvas
Challenges of Customer Identification and Entity Resolution
Identifying Customer Jobs and Needs
Importance of Customer-Centric Communication in Business
Importance of Customer Profile and Jobs to Be Done
Identifying and Addressing Emotional and Social Commitments in Jobs
Importance of Root Cause Analysis
The Role of a Chief Data Officer in Gaining Social Gain and Respect within a Business Organisation
Measuring the Benefit of a CDO
Responsibilities of a Chief Data Officer and Business Model Fit
Value Proposition and Customer Segments
Double-Sided Platforms
Multi-Sided Platform and Network Effects
Business Model Canvas and Value Proposition
Reinventing Your Business: Understanding the Value Proposition for Movie Goers
Research and Innovation in Business Context
Importance of Understanding Customer Needs and Jobs
Enterprise Level Problem Solving and Value Proposition
Importance of Measurement and Data Collection in Business Strategy
Framework for Customer Jobs and Contexts
Importance of Entrepreneurial Mindset in Business
Customer Value Proposition and Data Product Design
Howard Diesel welcomes everyone to the webinar series on marketing research analytics and designing a customer value proposition. Throughout this series, Howard shares that he will explore the importance of analytics in defining the customer value proposition, focusing on the shift from analysing demographics to identifying and addressing the jobs that customers need to do. The webinar will discuss collecting data to validate and verify the value proposition, building products that measure the value proposition and deliver value to customers, and providing a high-level introduction to the essential concepts of building data products to support the value proposition.
Figure 1 Value Proposition Glossary
Value Proposition and Business Model Canvas
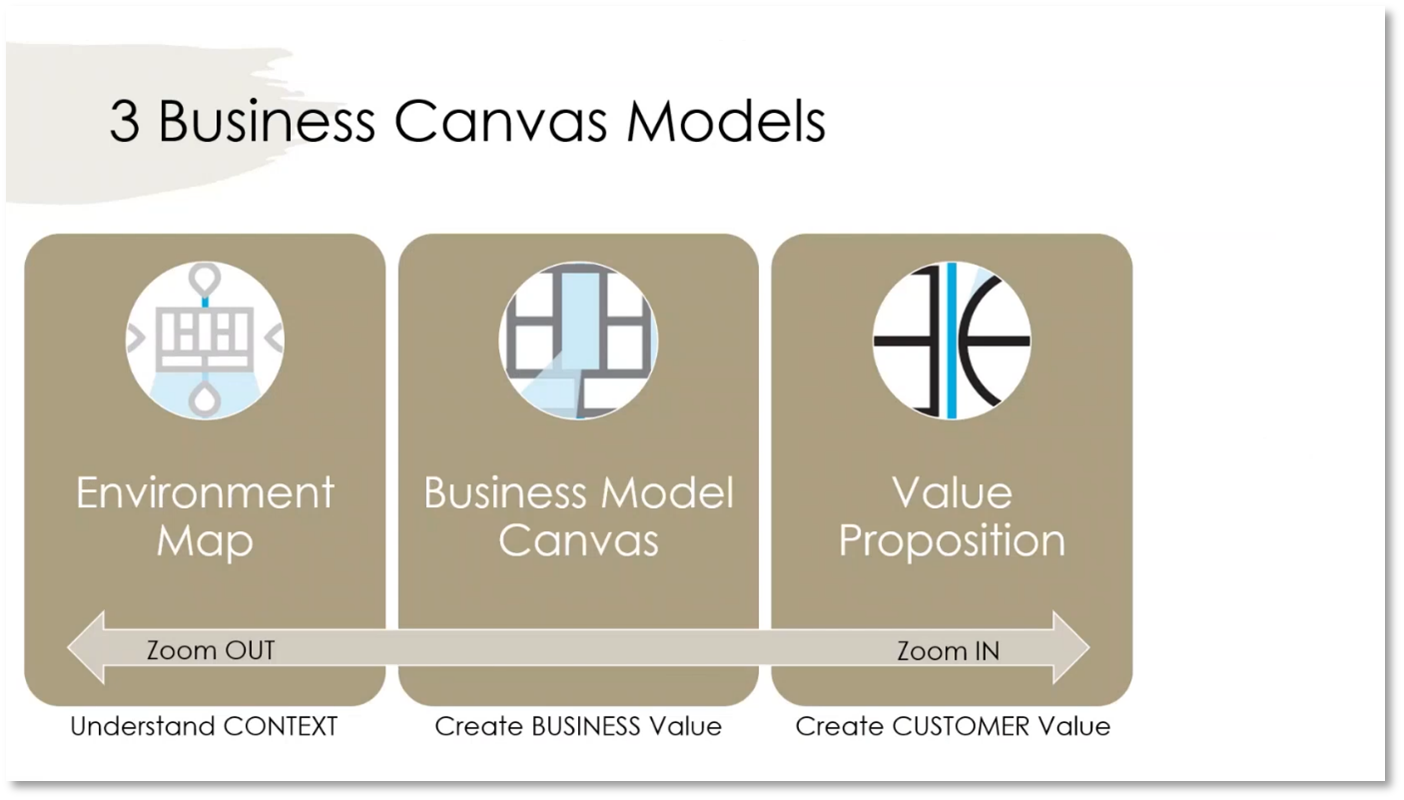
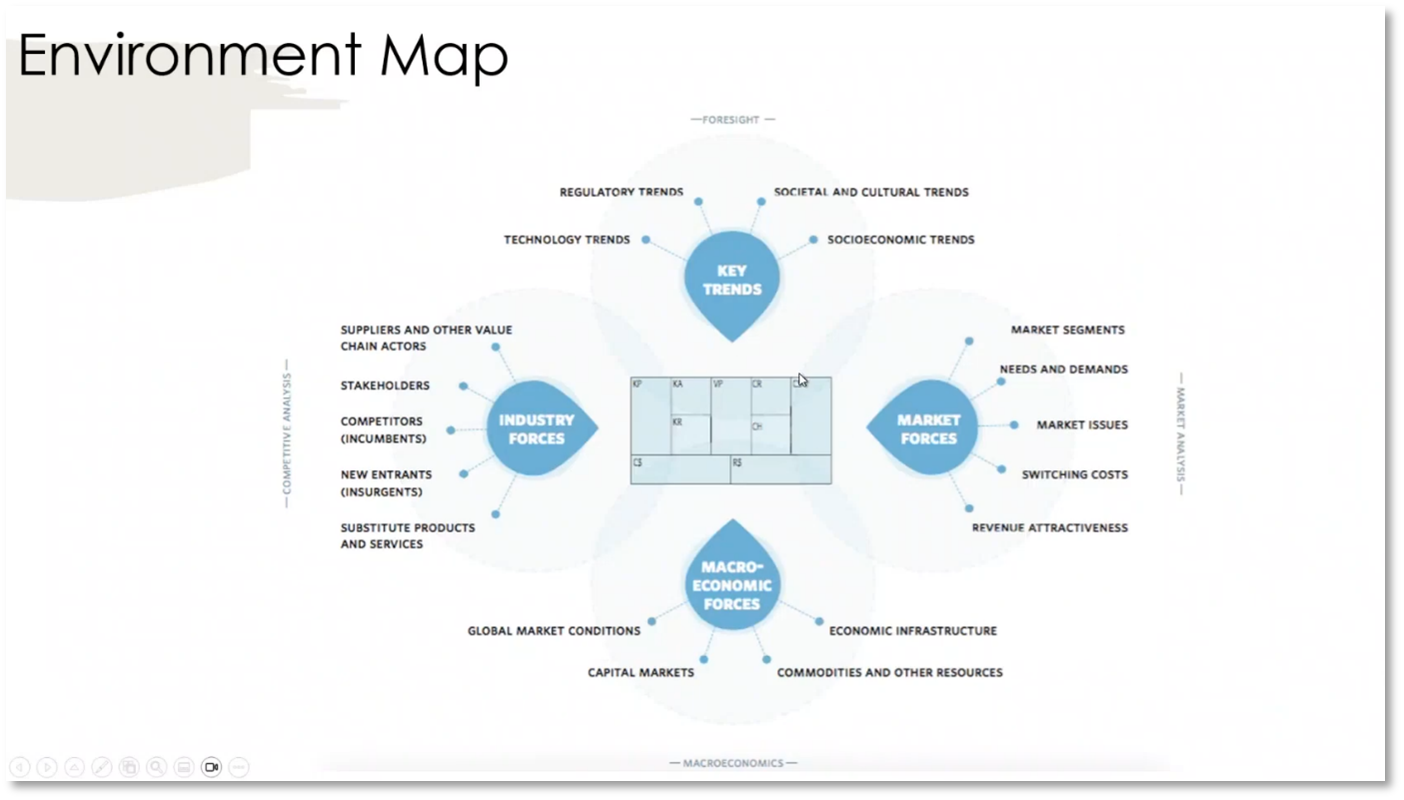
The value proposition plays a key role in delivering value to both the customer and the business. Understanding the customers' needs, wants, and aspirations is crucial to creating a successful value proposition, which is an integral part of the business model canvas and operates within a specific environmental context. Business architects and strategists work at the business model canvas level, while marketing is dedicated to building the customer value proposition. To create a successful value proposition, it is important to understand regulatory, technology, societal, cultural, socioeconomic, and industry trends.
Figure 2 Three Business Canvas Models
Figure 3 Environment Map
Business Model Canvas
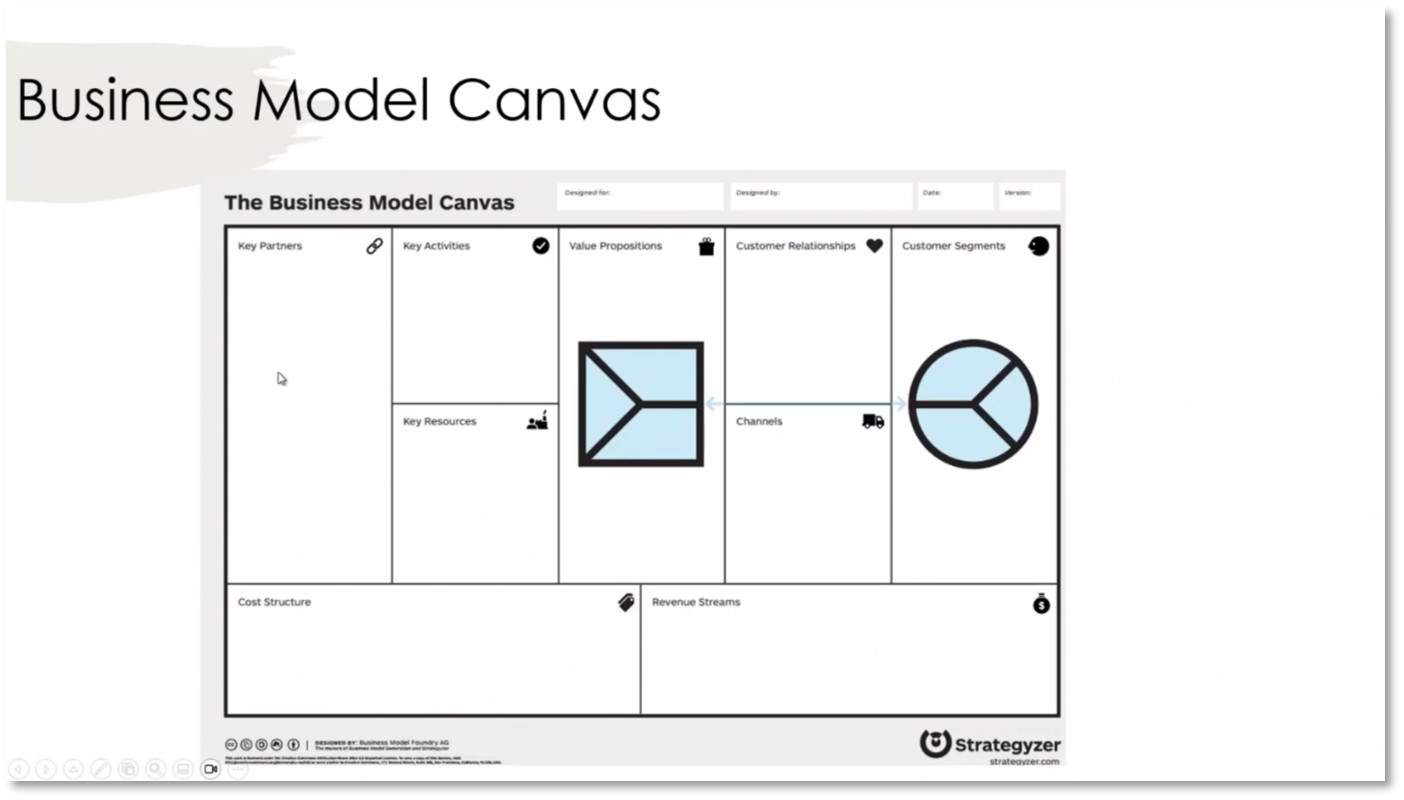
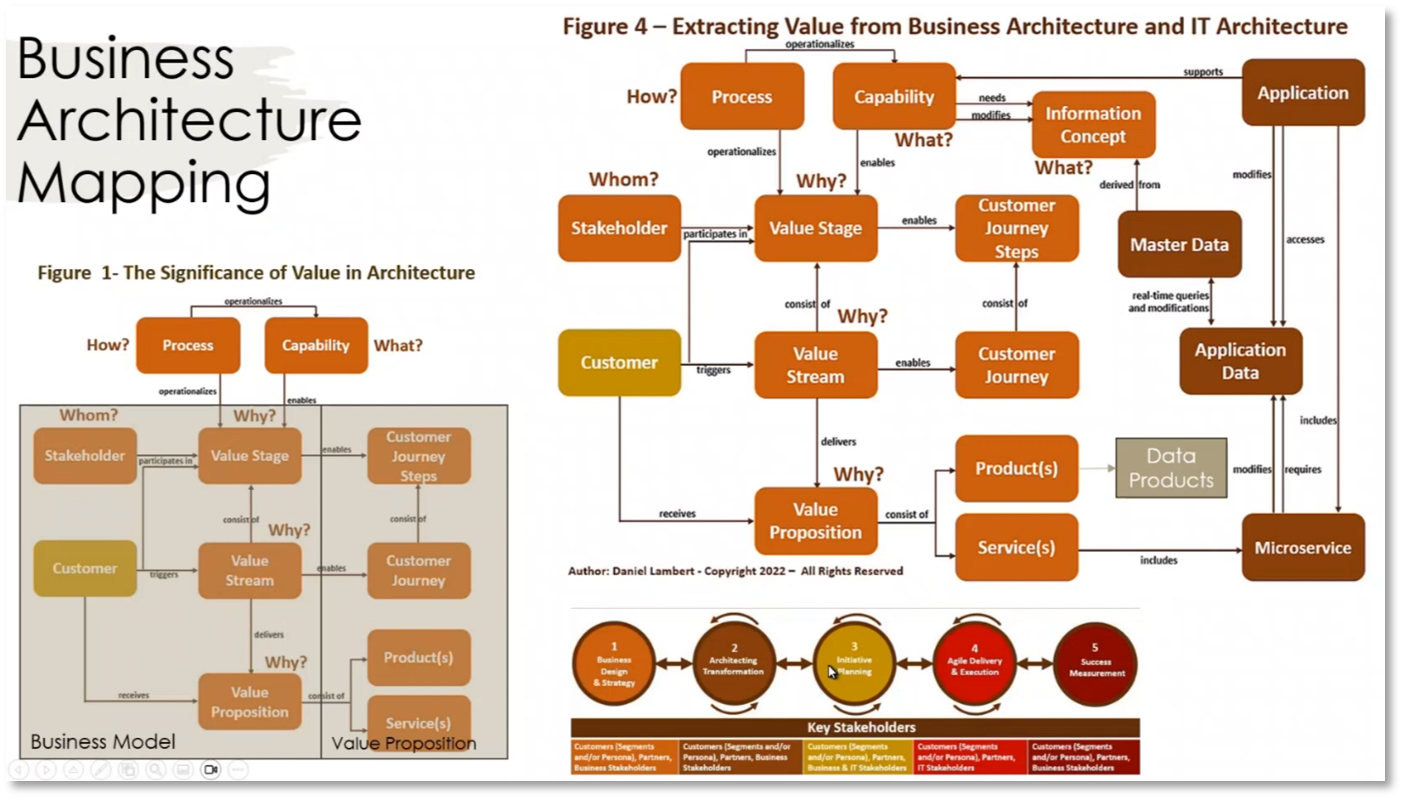
The business architecture assesses the business environment, covering political and economic factors. Meanwhile, the business model canvas aids in understanding the value proposition, key activities, resources, partnerships, customer relationships, and channels. In business architecture discussions, key activities and processes align with the capability map, while key resources encompass personnel, technology, and funding. Additionally, partnerships may be essential for outsourcing, and customer relationships and various channels are crucial for marketing and sustainability.
Figure 4 Business Model Canvas
Challenges of Customer Identification and Entity Resolution
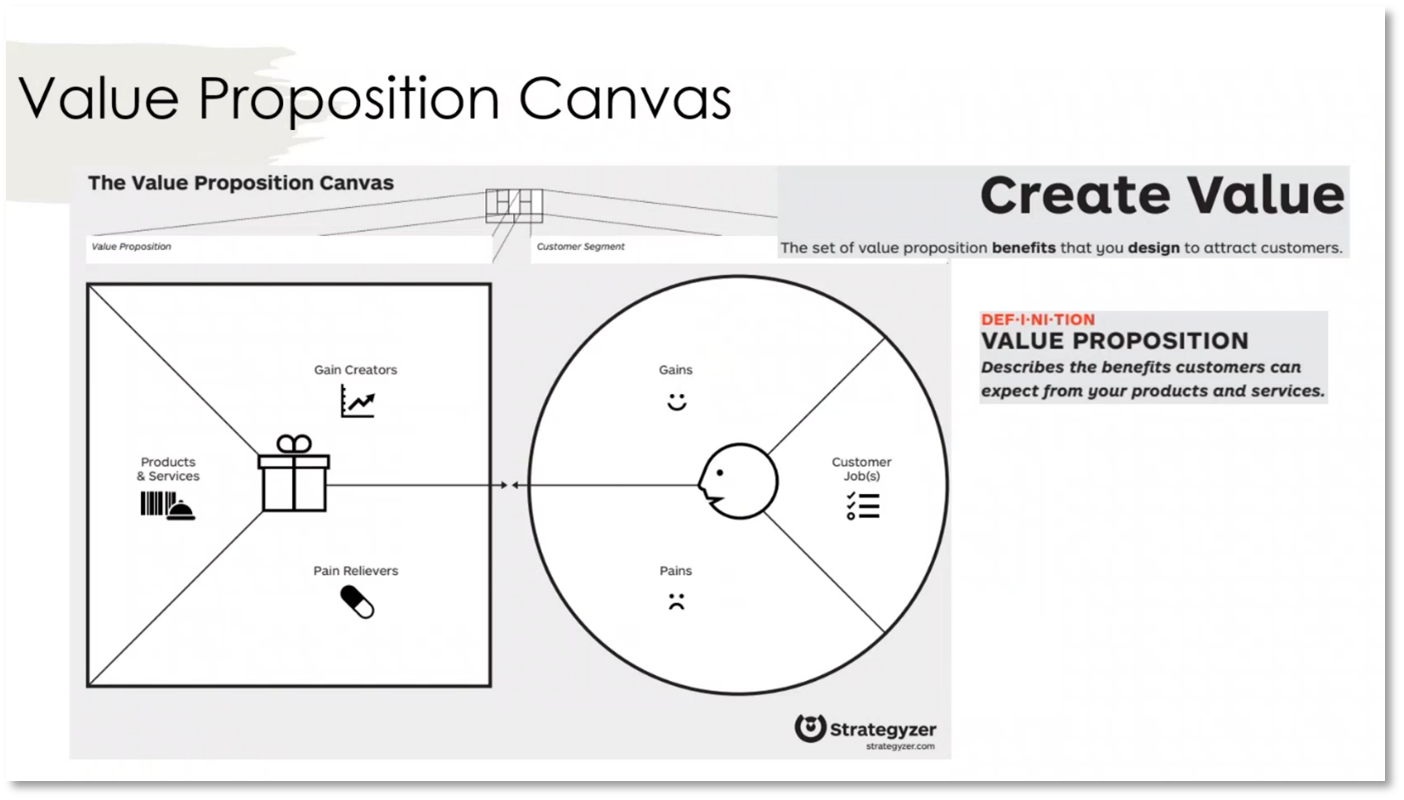
Howard outlines the challenges and best marketing practices of customer identification and attribution. It emphasises the importance of identifying customers across various channels, ensuring accurate counting across platforms, attributing value to campaigns, entity resolution in master data, evaluating business model cost and revenue, and creating value by identifying customer needs using the "jobs to be done" framework, with a specific focus on search engine optimisation (SEO) as an example.
Figure 5 Value Proposition Canvas
Identifying Customer Jobs and Needs
As a Chief Data Officer (CDO) or data professional, it's crucial to have the right product to develop data products for marketing purposes effectively. To start, defining the key jobs that both internal and external customers need to do is essential. Addressing customer pains and helping them achieve gains should be the focus of customer jobs. It is vital to create a customer profile and find a product that addresses their pain relief and gains needs. Data professionals, who may undergo job changes, require products and services that can adapt to their evolving needs, making it crucial to understand their long journey with changing jobs.
Importance of Customer-Centric Communication in Business
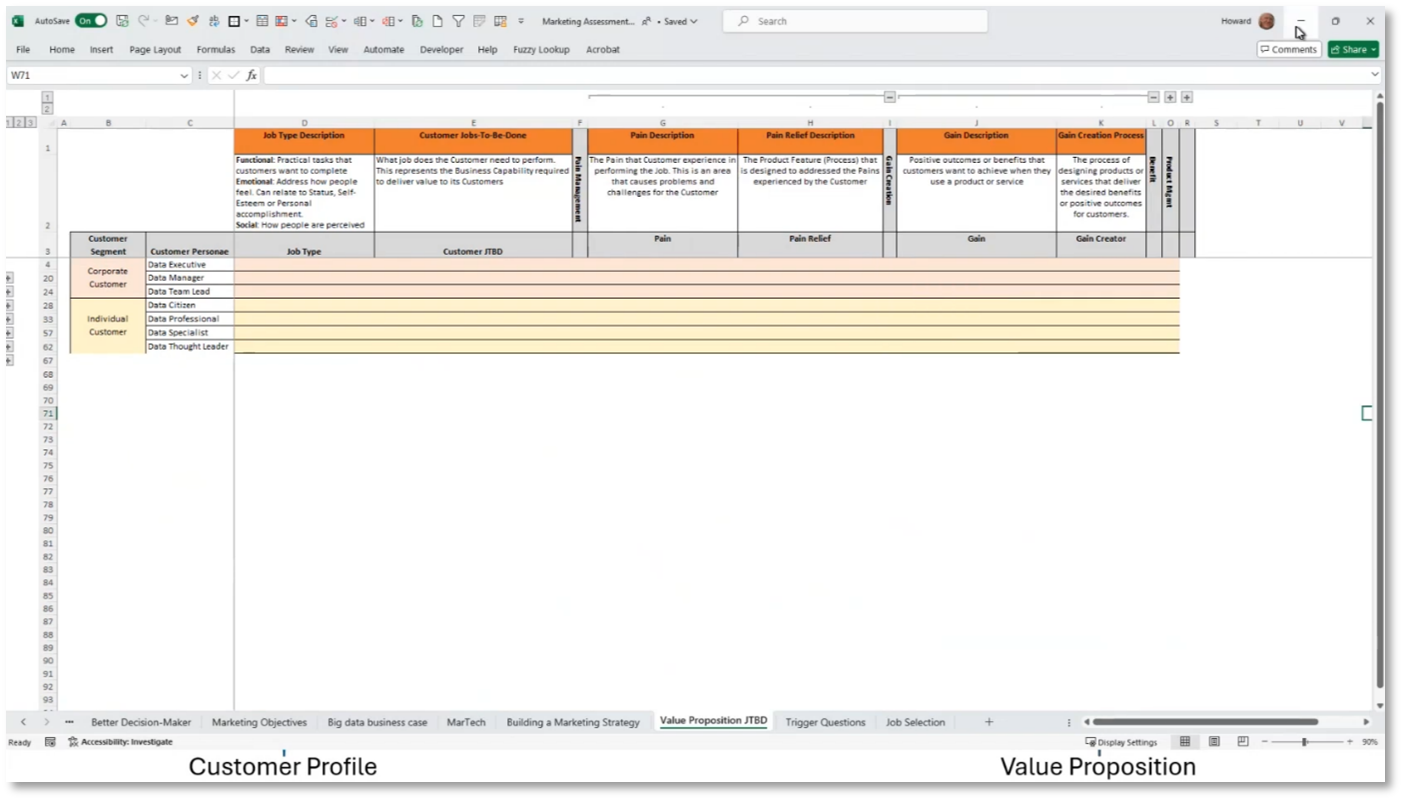
To effectively market products and services, it is important to ask questions and address the pains and gains of customers. Business Architects are responsible for defining the value proposition, while marketing professionals specialise in personas and customer journeys to determine the right products and services. Understanding and enabling the customer is essential for developing an Enterprise architecture, even for those not directly involved in marketing. For data products, aligning the value proposition with the customer journey and effectively communicating with the customer is crucial. Utilising an Excel template and collecting data are essential for building value propositions and understanding customer personas and their needs.
Figure 6 Business Architecture Mapping
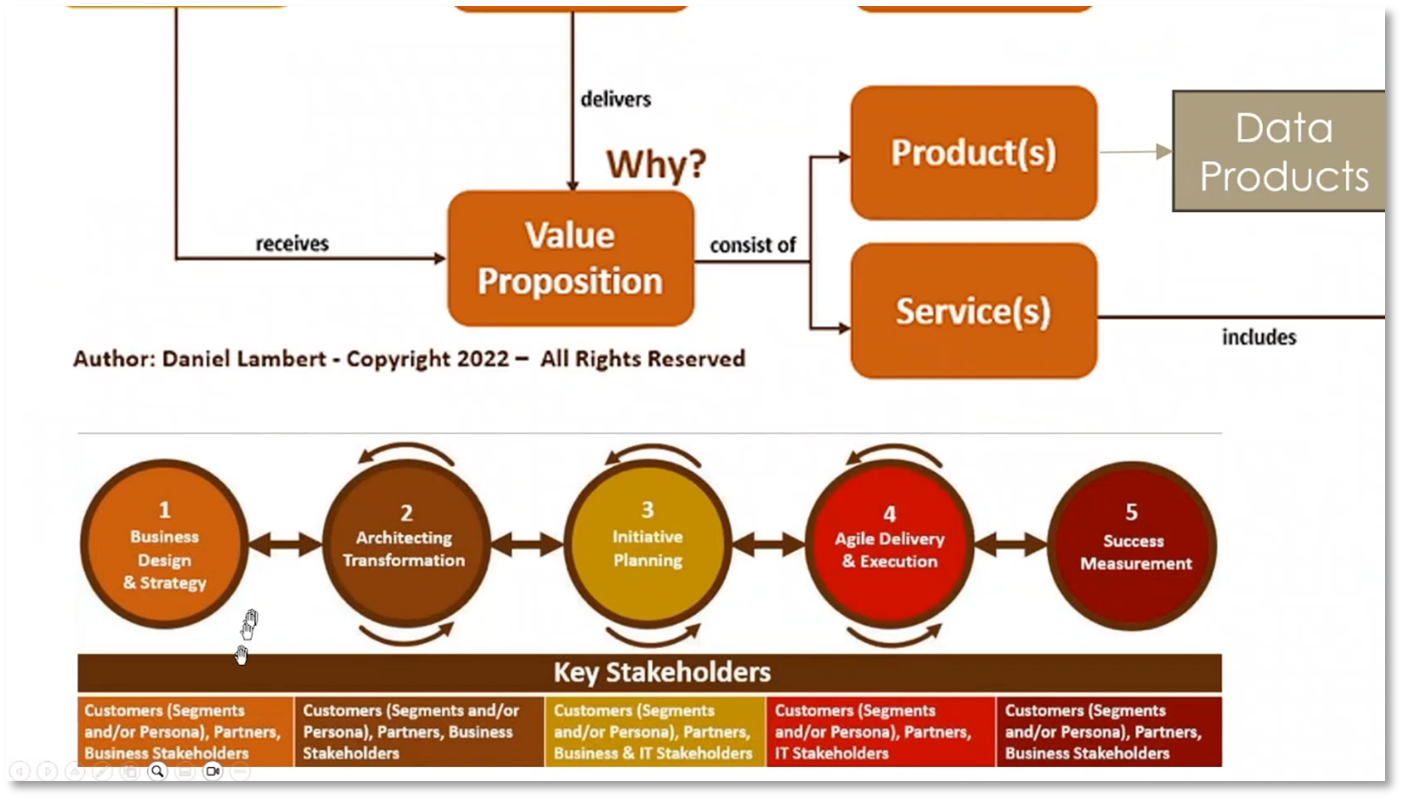
Figure 7 Business Architecture Mapping continued
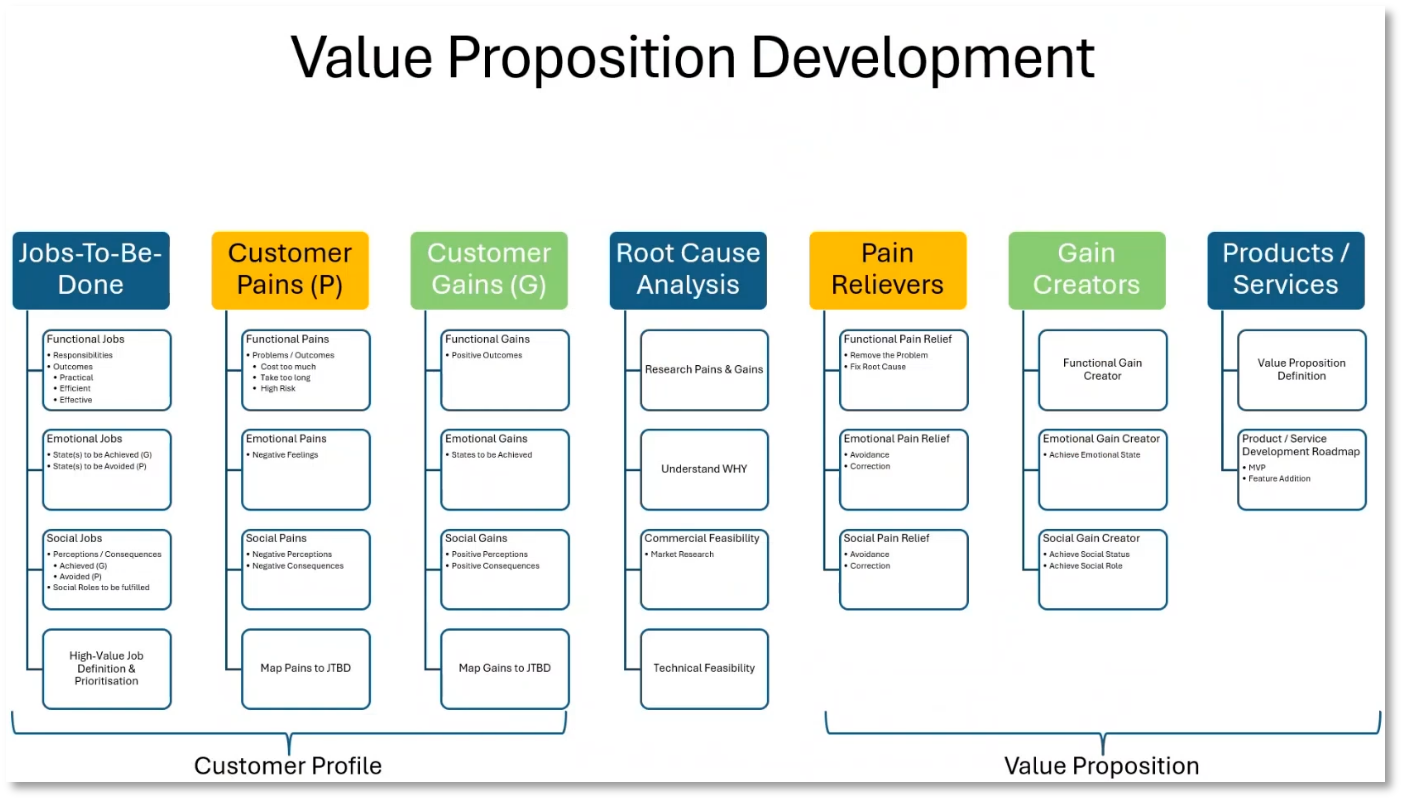
Figure 8 Value Proposition Development
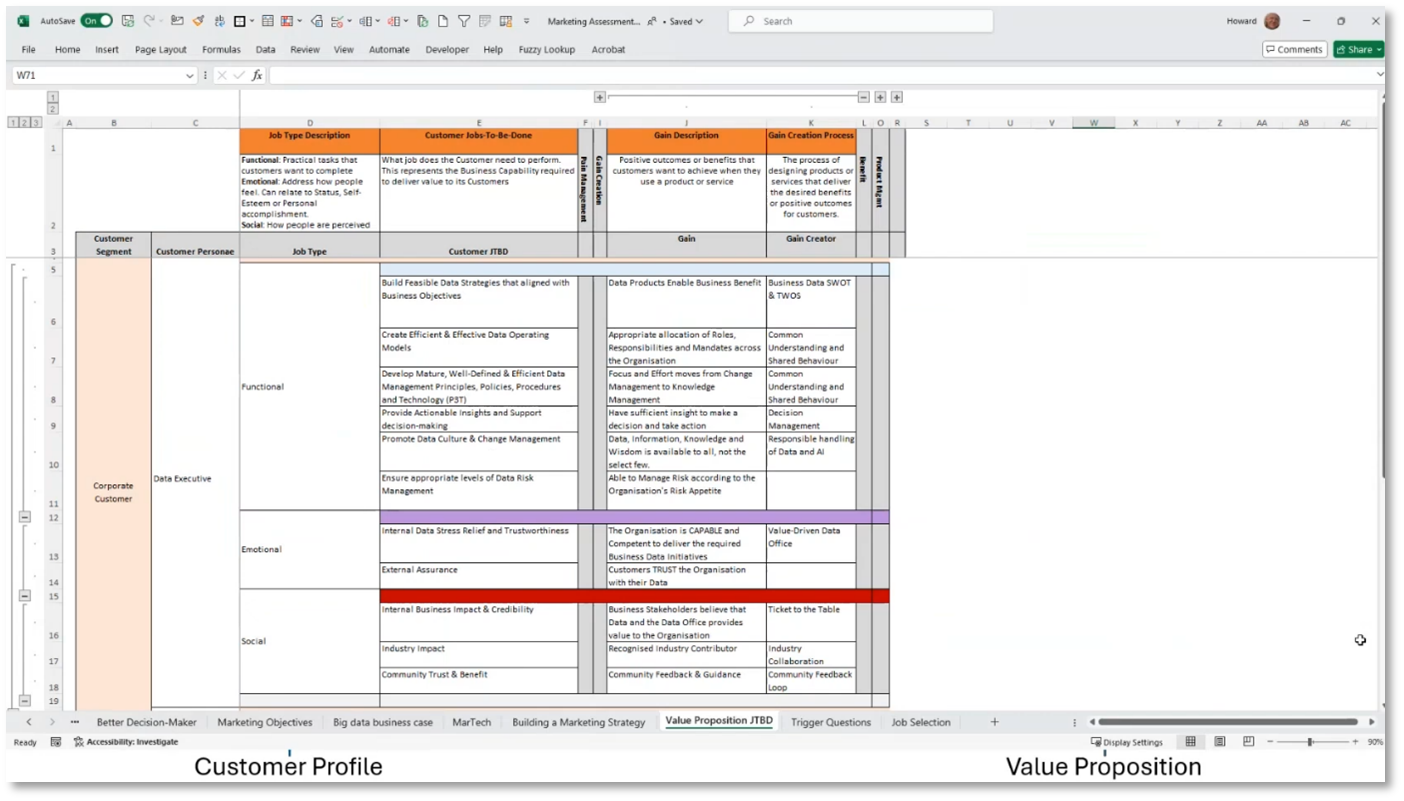
Figure 9 Customer Profile and Value Proposition
Importance of Customer Profile and Jobs to Be Done
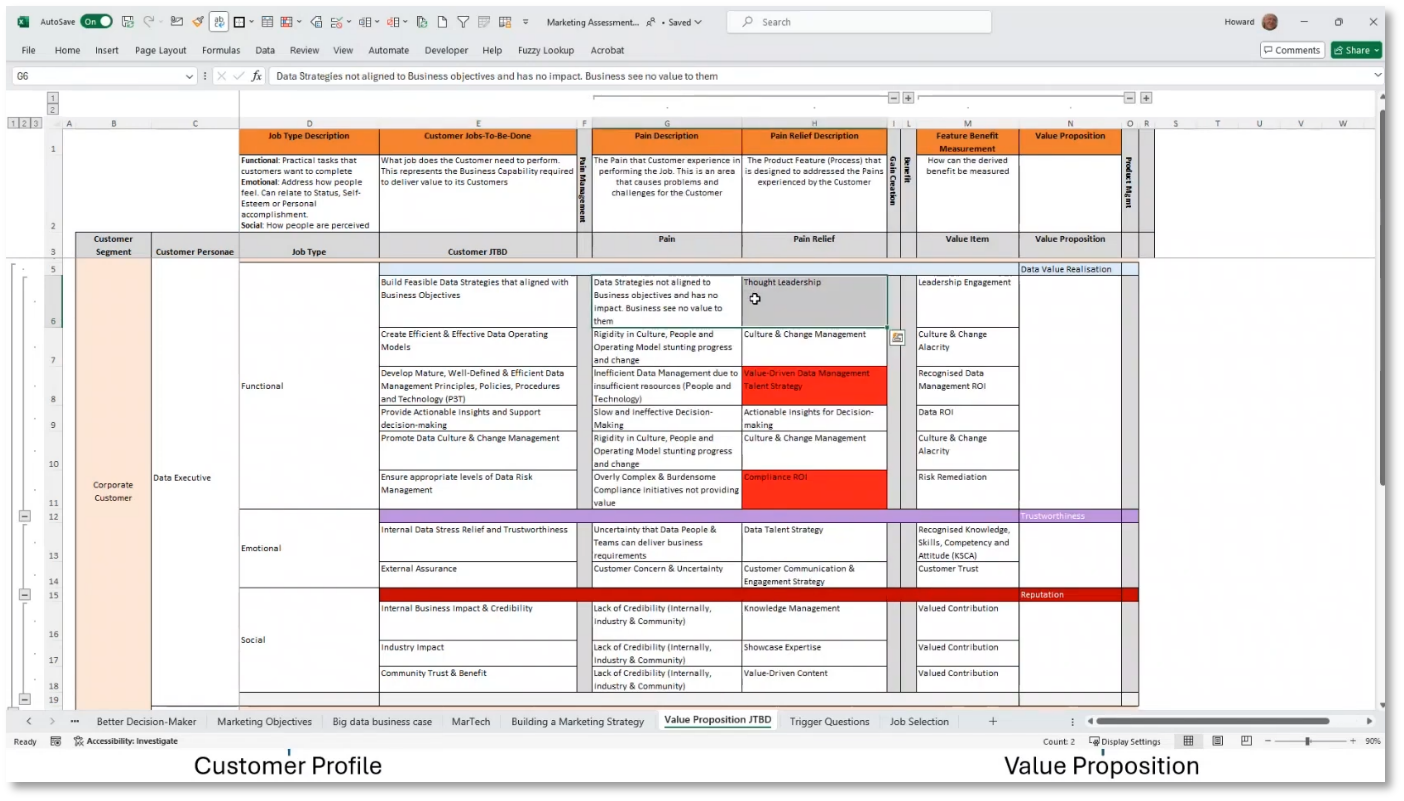
Understanding the customer profile and identifying the core jobs to be done are critical elements for the success of a Chief Data Officer (CDO). It's important to recognise that addressing emotional and social aspects is equally essential beyond functional tasks. Emotional states like earning trust and demonstrating value can significantly impact a CDO's credibility and longevity. Moreover, social responsibilities, including community impact and ethical data management, play a pivotal role in ensuring the success of a CDO.
Figure 10 Customer Profile and Jobs to Be Done
Identifying and Addressing Emotional and Social Commitments in Jobs
Consider the emotional and social aspects of any job and the potential consequences if these are not met. Identify the "jobs to be done" and associated pains, such as high costs and long wait times. Seek solutions to alleviate these pains and achieve positive outcomes, including functional and emotional gains in job performance and team success. Delivering good value to both internal and external customers can lead to positive social gains and perceptions. It's essential to align products with the jobs to be done and address any remaining pains by understanding customer profiles and seeking confirmation of their experiences.
Importance of Root Cause Analysis
The importance of root cause analysis in understanding the underlying reasons for positive and negative outcomes in different functions is emphasised. Assessing the commercial and technical feasibility before developing products and services to address these outcomes is crucial. Defining the gains and pains is essential before promoting products and services. Additionally, the significance of validating positive outcomes and seeking social gains such as trust and word-of-mouth promotion is highlighted, as these substantially impact the commercial environment and the perception and use of data and services.
The Role of a Chief Data Officer in Gaining Social Gain and Respect within a Business Organization
As a Chief Data Officer (CDO), it's crucial to establish trust and gain social acceptance within the organisation while playing a key role in developing business strategy and creating revenue-generating data products. Demonstrating the value of your work through successful delivery on challenges with the appropriate budget and technology is essential, as is gaining mutual respect, especially since CDOs are often new and may not have immediate recognition for their capabilities. Defining the characteristics of an effective CDO and data professional is also crucial for gaining social acceptance and impressing business leaders.
Measuring the Benefit of a CDO
The importance of measuring the benefits of a Chief Data Officer (CDO) is discussed, and Howard emphasises using an Excel spreadsheet for effective measurement. The core responsibilities of a CDO include defining a data strategy, building an effective operating model, ensuring efficient operations, providing actionable insights, promoting a data-driven culture, and reducing risk. The value of a CDO's work can be measured using metrics such as data value realisation, data office Return on Investment (ROI), and data ROI. The social impact of a CDO involves contributing to industry standards, being a recognised industry contributor, and impacting the community by participating in conferences and gaining respect within the industry.
Figure 11 Customer Profile and Value Proposition continued
Responsibilities of a Chief Data Officer and Business Model Fit
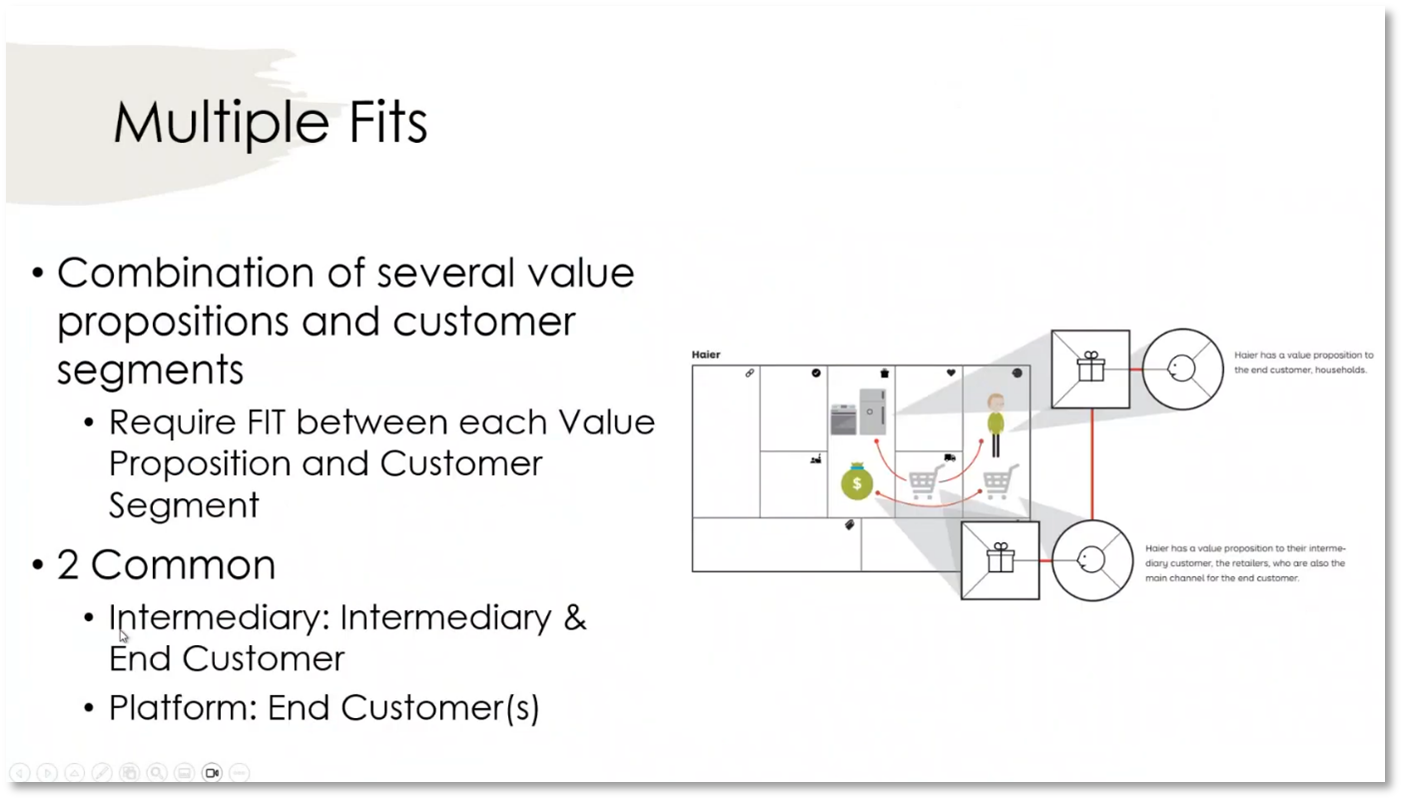
A Chief Data Officer (CDO) plays a crucial role in an organisation by gaining respect and credibility, leading to people seeking guidance and sharing data. Data collection, interviews, and research are necessary to determine job requirements. It's important to consider published articles showcasing CDO responsibilities and achievements. Addressing customer challenges requires clearly understanding the value proposition and defining products and services. Three stages of fit – customer profile fit, product-market fit, and business model fit – are essential to align with customer needs and profitability. Continuous assessment of the business model's fit, including paper, market, and bank, is necessary. Furthermore, multiple fits can exist at the business model level, as seen in an organisation's value proposition to end and intermediary customers.
Figure 12 Three stages of FIT
Figure 13 Multiple Fits
Value Proposition and Customer Segments
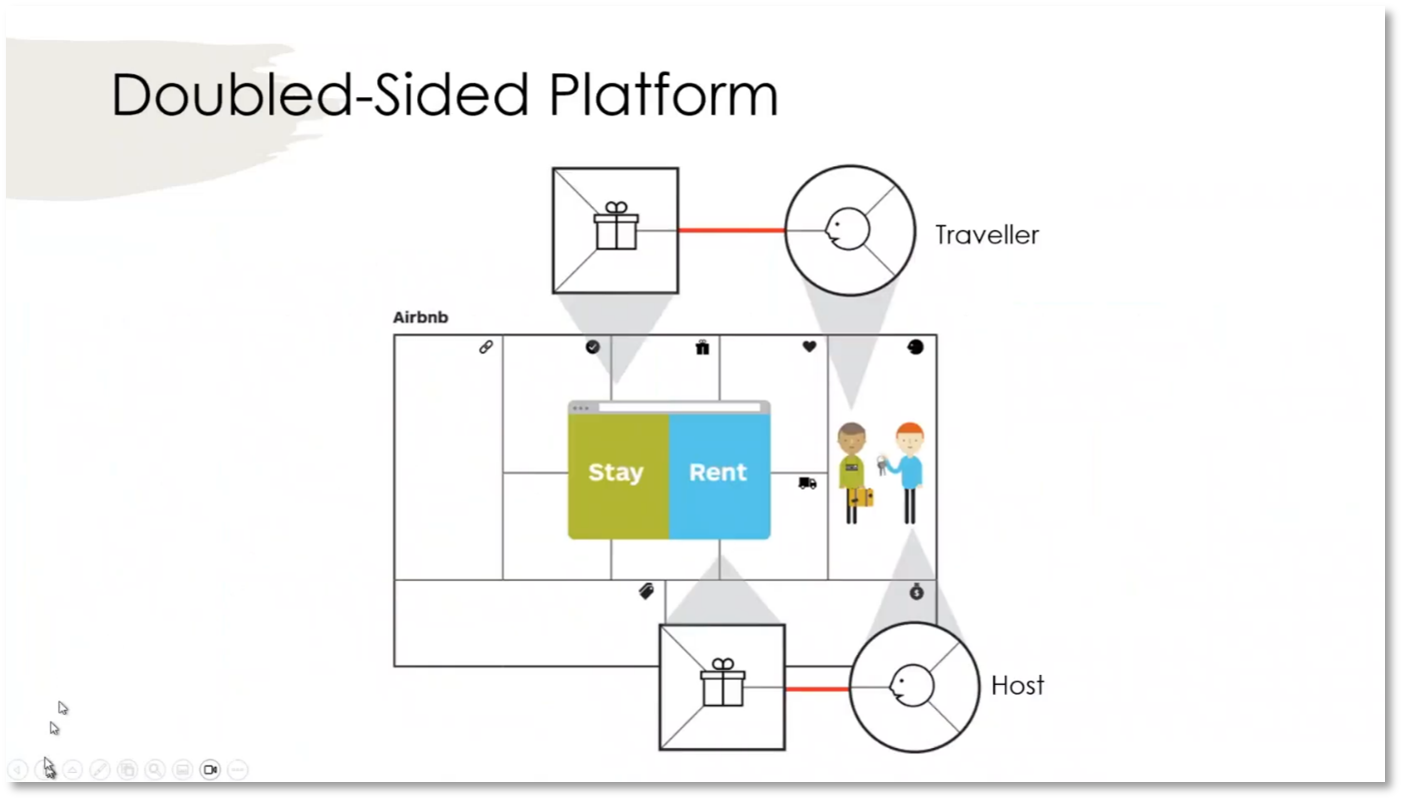
Understanding the diverse value propositions of different retailers presents challenges in creating customer profiles. It is essential to align each value proposition with the corresponding customer segment. Common customer segments include intermediaries, who may act on behalf of a business, and end customers. The complexity increases when dealing with double-sided customers, like hosts and travellers on a BNB platform, as they have distinct value propositions but must collaborate for the platform's success. Similarly, corporate customers and individuals from different customer segments must collaborate for mutual business success.
Figure 14 Platforms
Figure 15 Double-Sided Platform
Double-Sided Platforms
Howard highlights the importance of collaborating on data talent strategy and individual skills, emphasising the interdependence in a double-sided platform where one person relies on another to achieve different outcomes. The Chief Data Officer (CDO) necessitates an effective data operating model and skilled professionals, while individuals rely on CBO strategy and management. This interdependence is illustrated through healthcare and funding scenarios, emphasising the need to demonstrate value to all involved parties. Additionally, Howard discusses with an attendee the transition from a product to a platform, with Uber as an example of a two-sided network.
Multi-Sided Platform and Network Effects
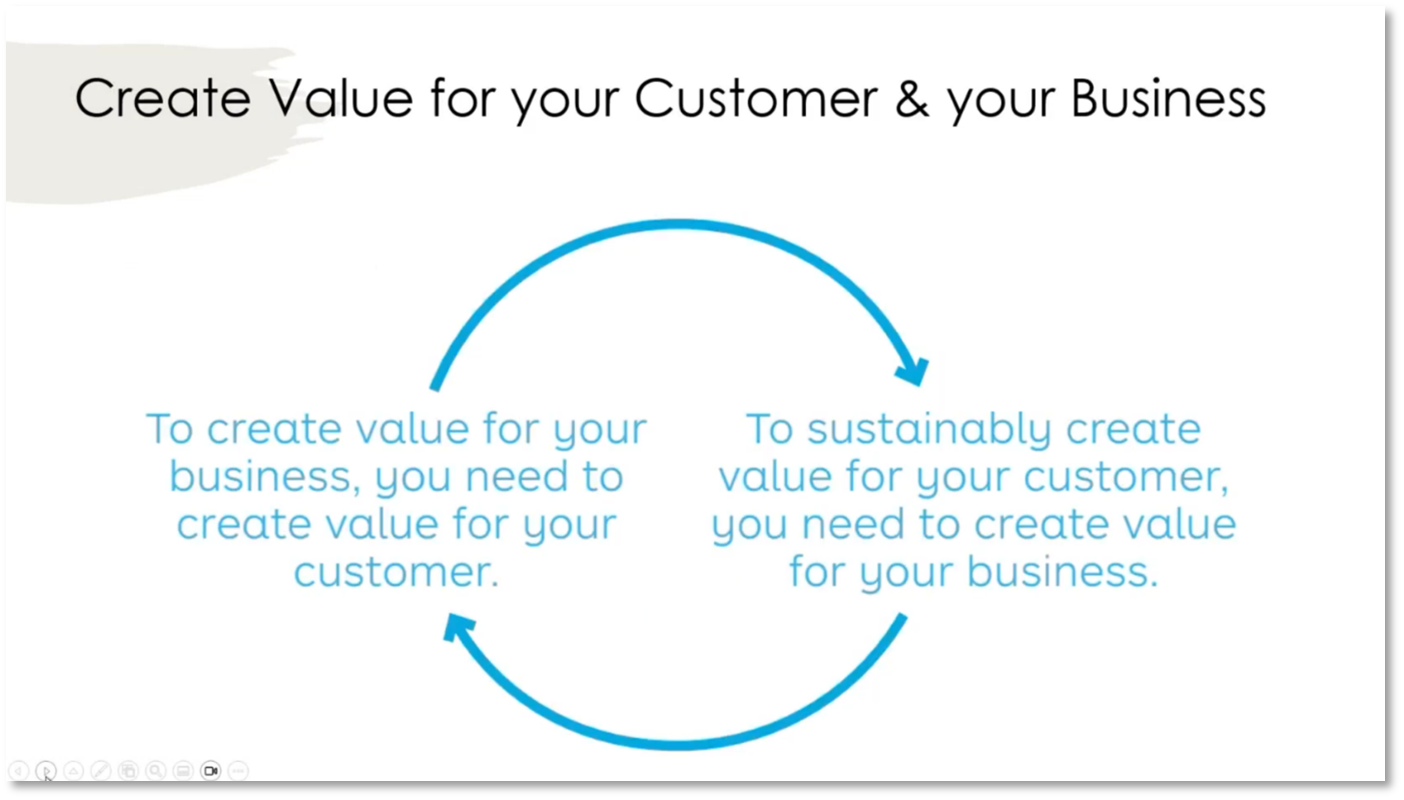
The concept of a multi-sided platform involves interconnected parties, such as hospitals, doctors, and patients in healthcare, leading to network effects where the platform's value increases with more users. Transitioning from a product to a platform enables double-sided or multi-sided interactions, creating value within an interdependent business model. Customising data products for different perspectives, such as patients, practitioners, hospitals, and insurers, is crucial for providing customer value. Creating value for the customer is essential for the business, as the two are interconnected within the business model and environment map. This approach focuses on customer value and considers the broader business model and environment map to achieve desired outcomes.
Figure 16 Create Value for your Customer & your Business
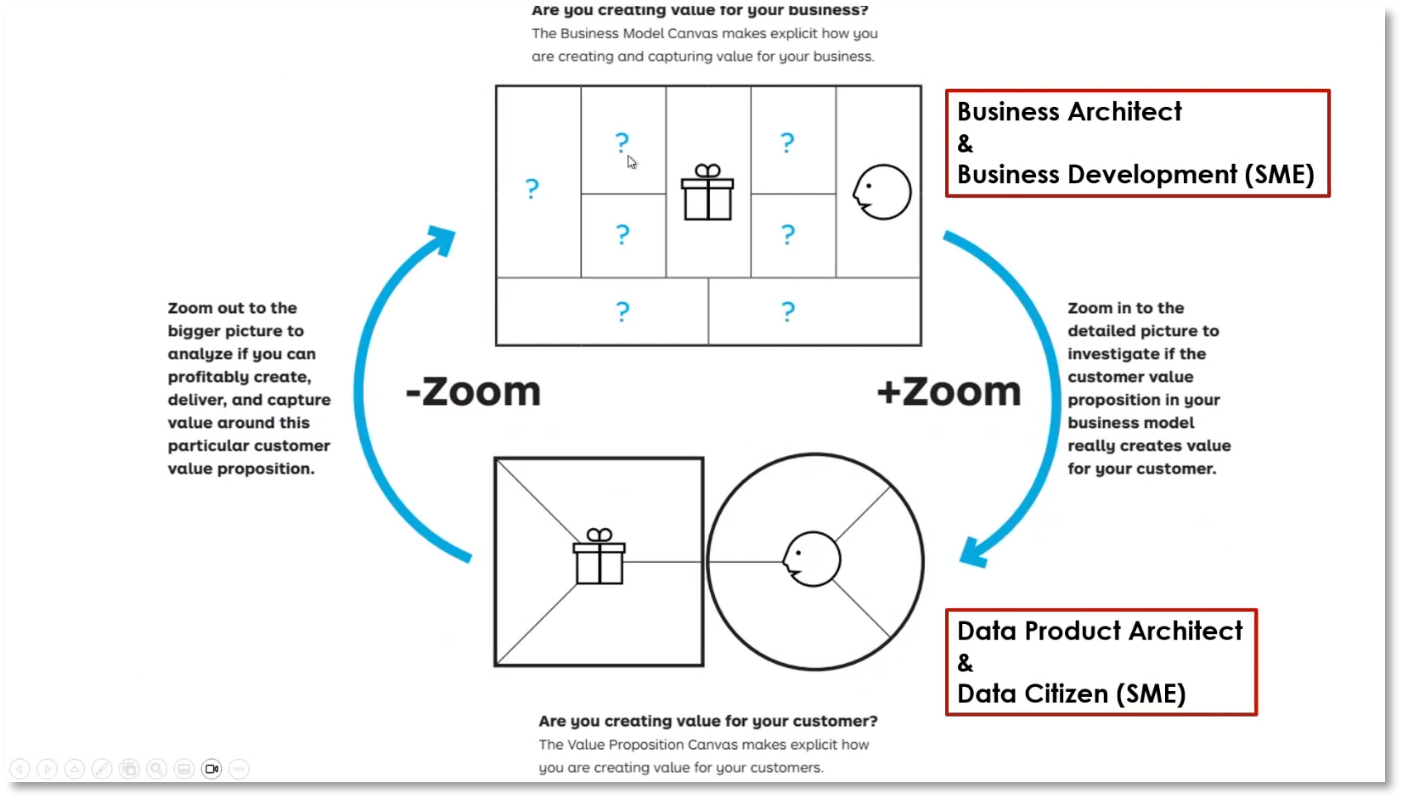
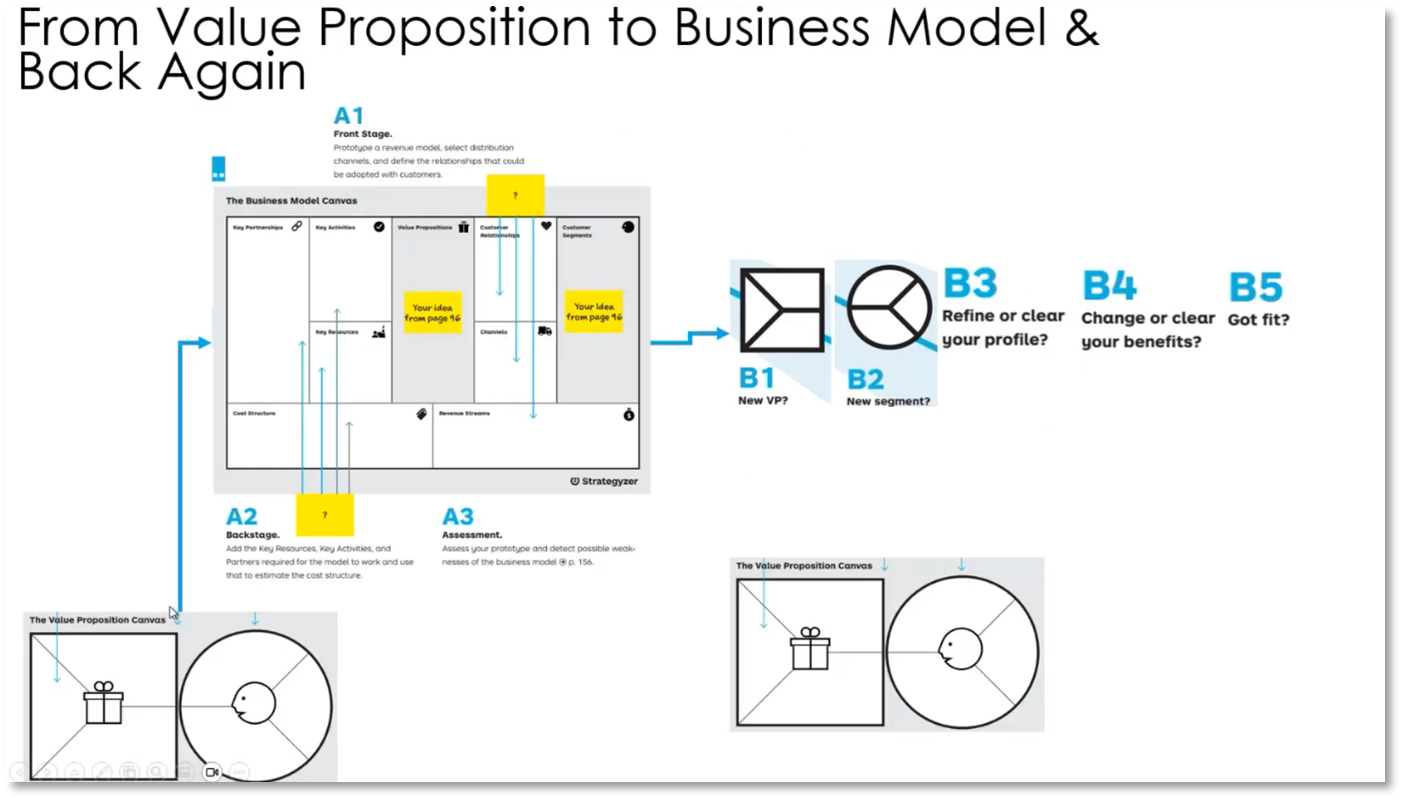
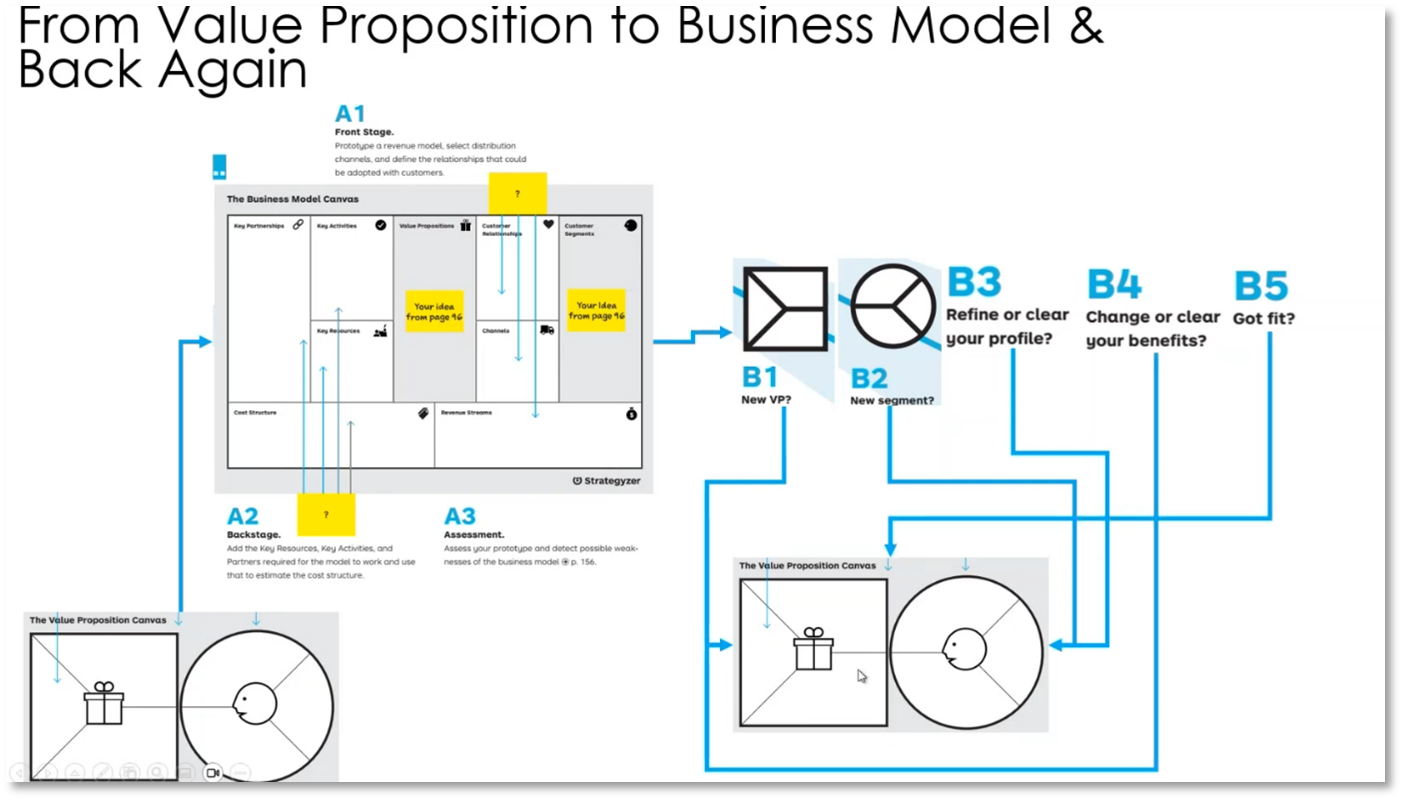
Business Model Canvas and Value Proposition
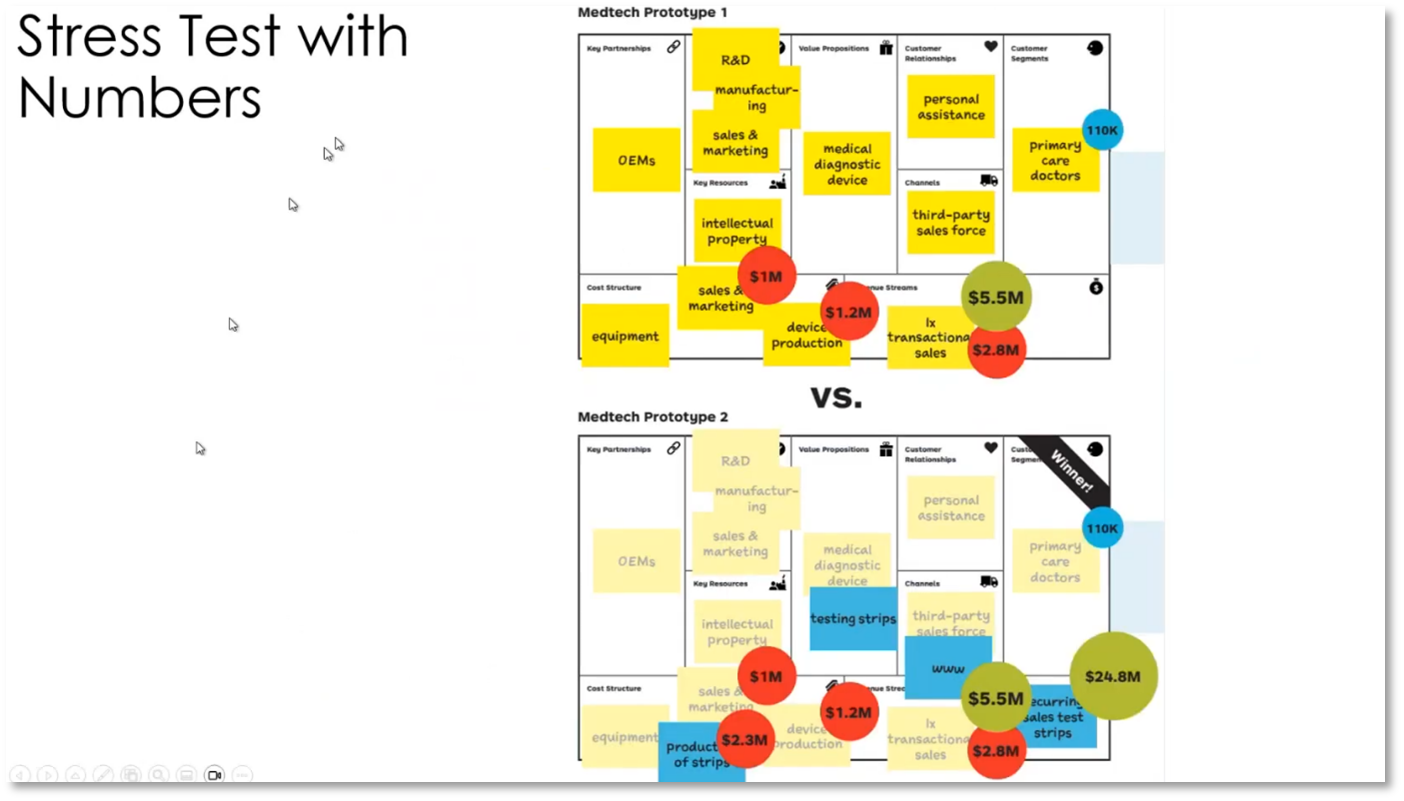
The business model canvas and value proposition are influenced by the environment, with business architects and business development working at one level and data product and marketing personnel at another. Constant iterations and feedback are crucial for identifying added value and understanding the customer's journey. The process includes moving from a value map to a business model, assessing profitability, and making necessary adjustments, such as evaluating the need for a new value proposition, analysing segments, refining profiles, changing benefits, and ensuring the right fit for customers. Stress tests with numbers are used to assess the potential impact of changes. Ensuring the "fit" involves checking for features, addressing pains relating to specific jobs, and finding the right balance for customers. Data is critical in scaling and refining the business model and value proposition.
Figure 17 Business Model Canvas and Value Proposition
Figure 18 Business Model Canvas and Value Proposition continued
Figure 19 Business Model Canvas and Value Proposition continued
Figure 20 Stress Test with Numbers
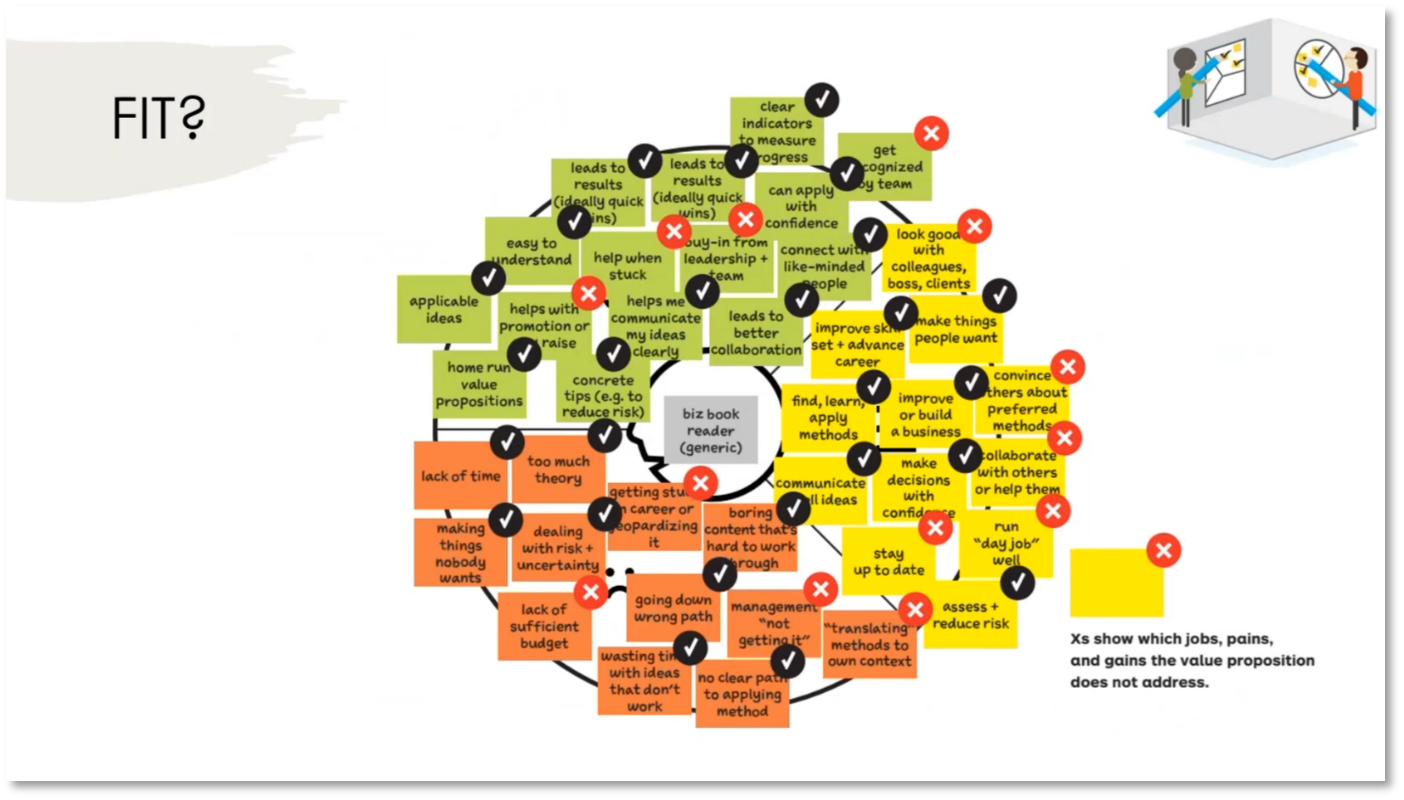
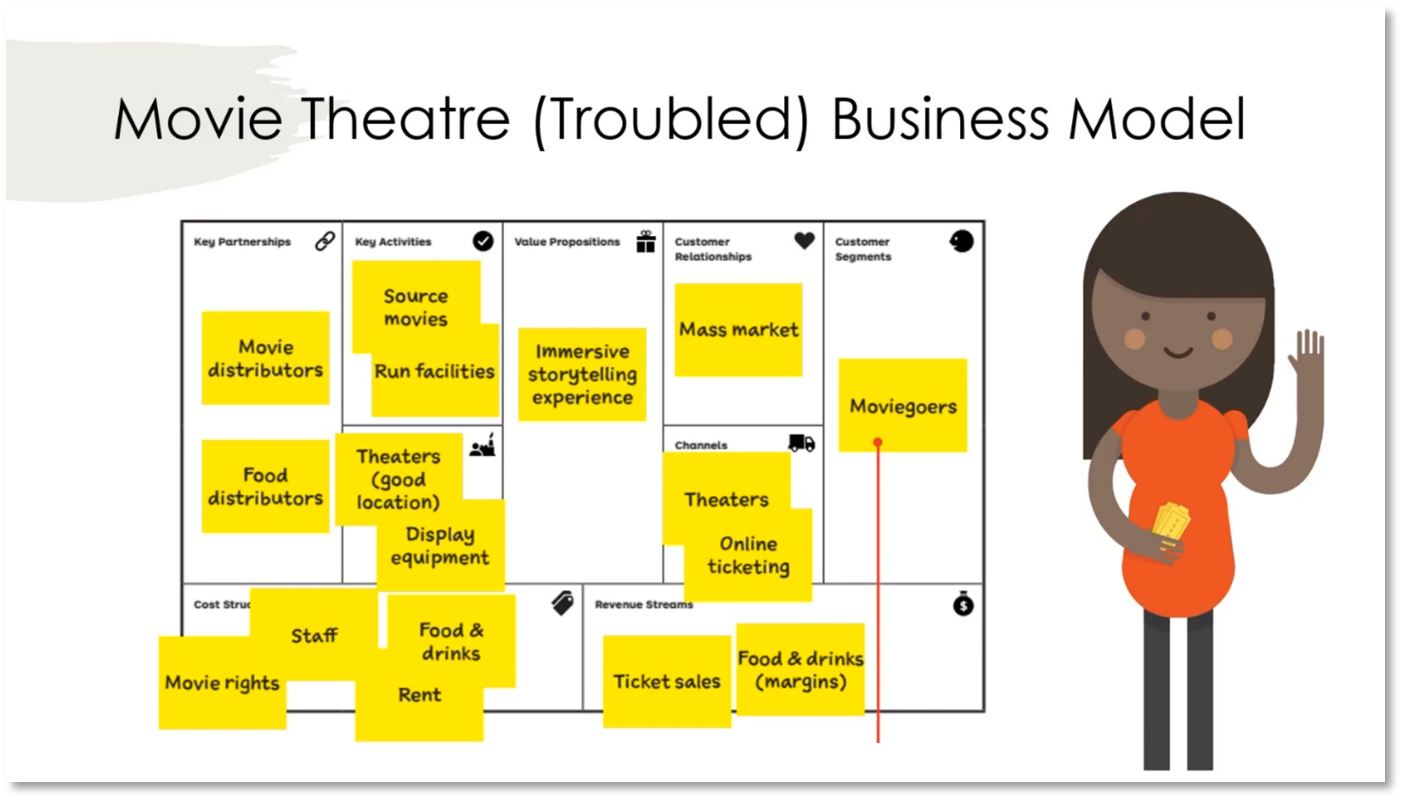
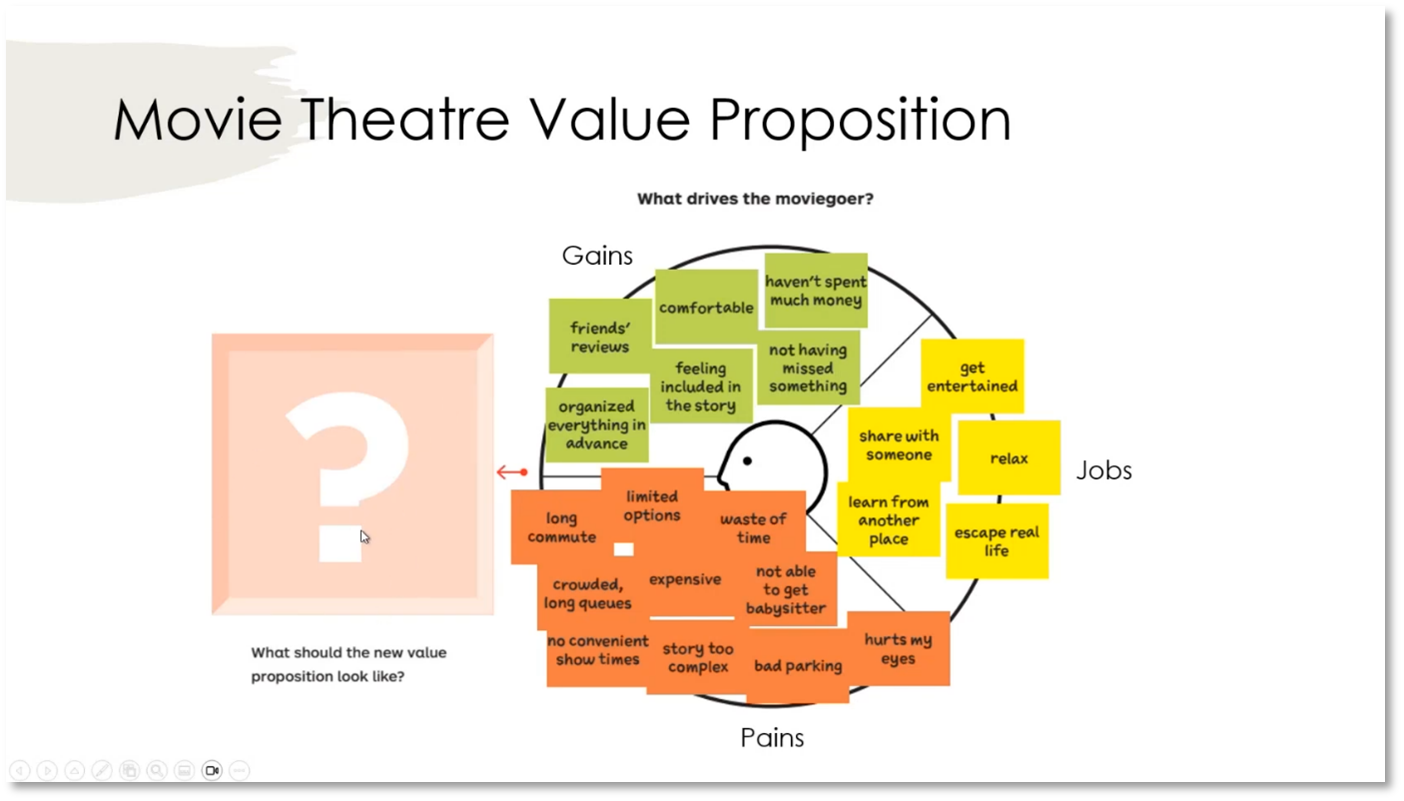
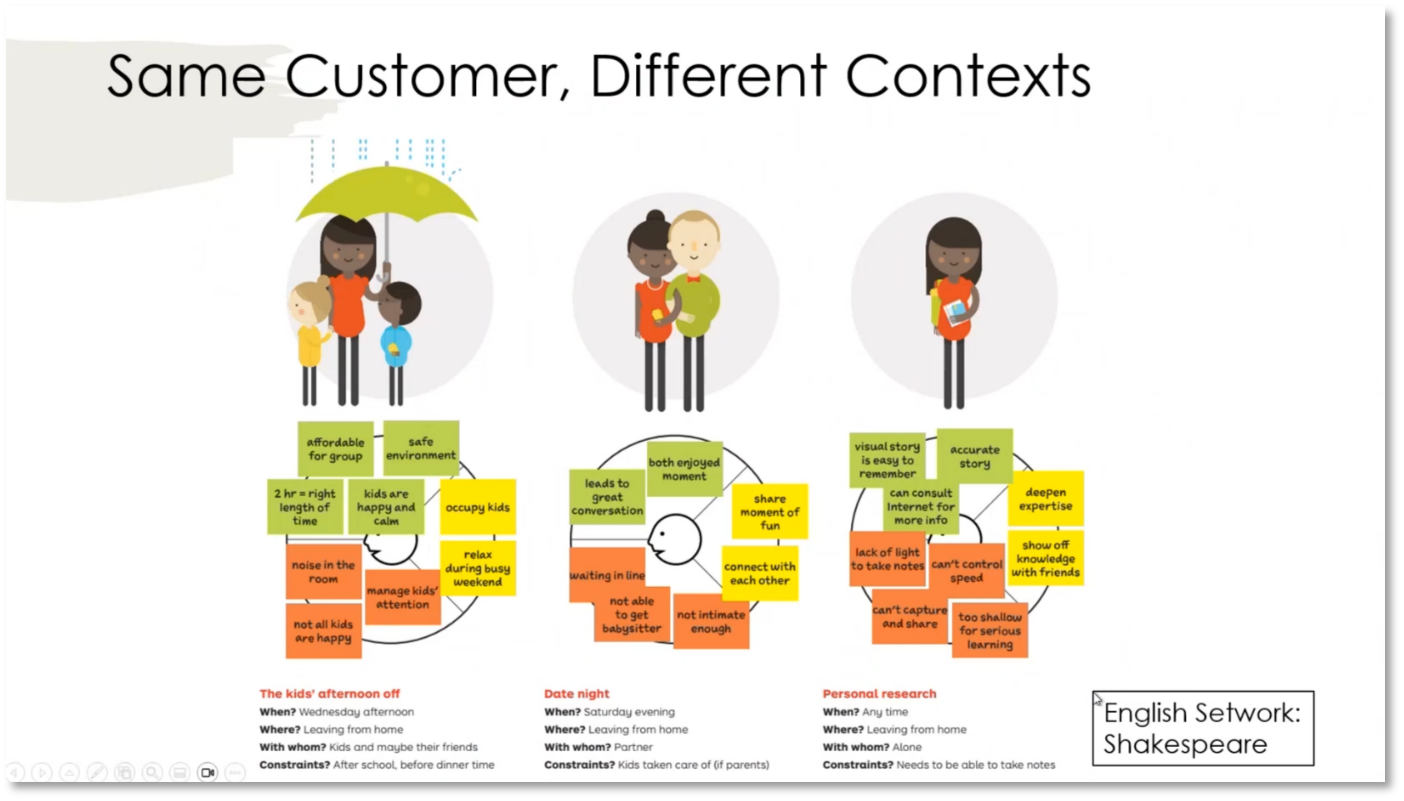
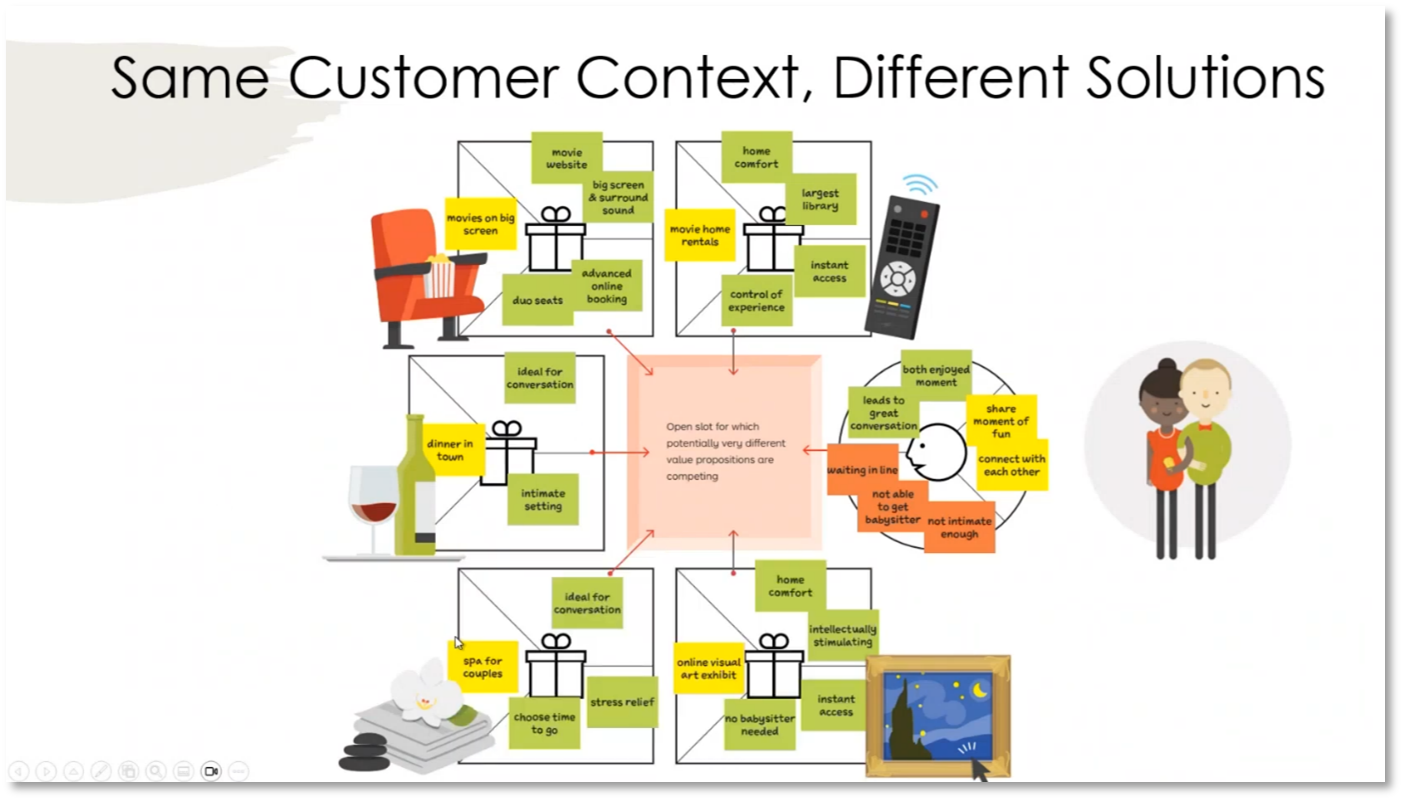
Reinventing Your Business: Understanding the Value Proposition for Movie Goers
Movie theatres are currently facing challenges in attracting customers due to high prices and inconveniences. To address this, it's important to analyse the value proposition for moviegoers by understanding the jobs they are trying to accomplish and the pains they experience when going to the theatre. Different customer contexts, such as family outings, date nights, and personal research, require distinct value propositions to cater to their needs. Movie theatres should explore offering alternative benefits, such as educational experiences and cultural enrichment, beyond traditional entertainment to attract customers.
Figure 21 FIT?
Figure 22 Movie Theatre (Troubled) Business Model
Figure 23 Movie Theatre (Troubled) Business Model continued
Research and Innovation in Business Context
Research in personal and business contexts, such as reading, watching movies, or attending AR exhibitions, can deepen understanding and drive innovation. Prioritisation using tools like Excel is crucial for managing tasks effectively, and a Chief Data Officer (CDO) needs to focus on deliverables to build credibility in the business setting.
Figure 24 Same Customer, Different Contexts
Figure 25 Same Customer Contexts, Different Solutions
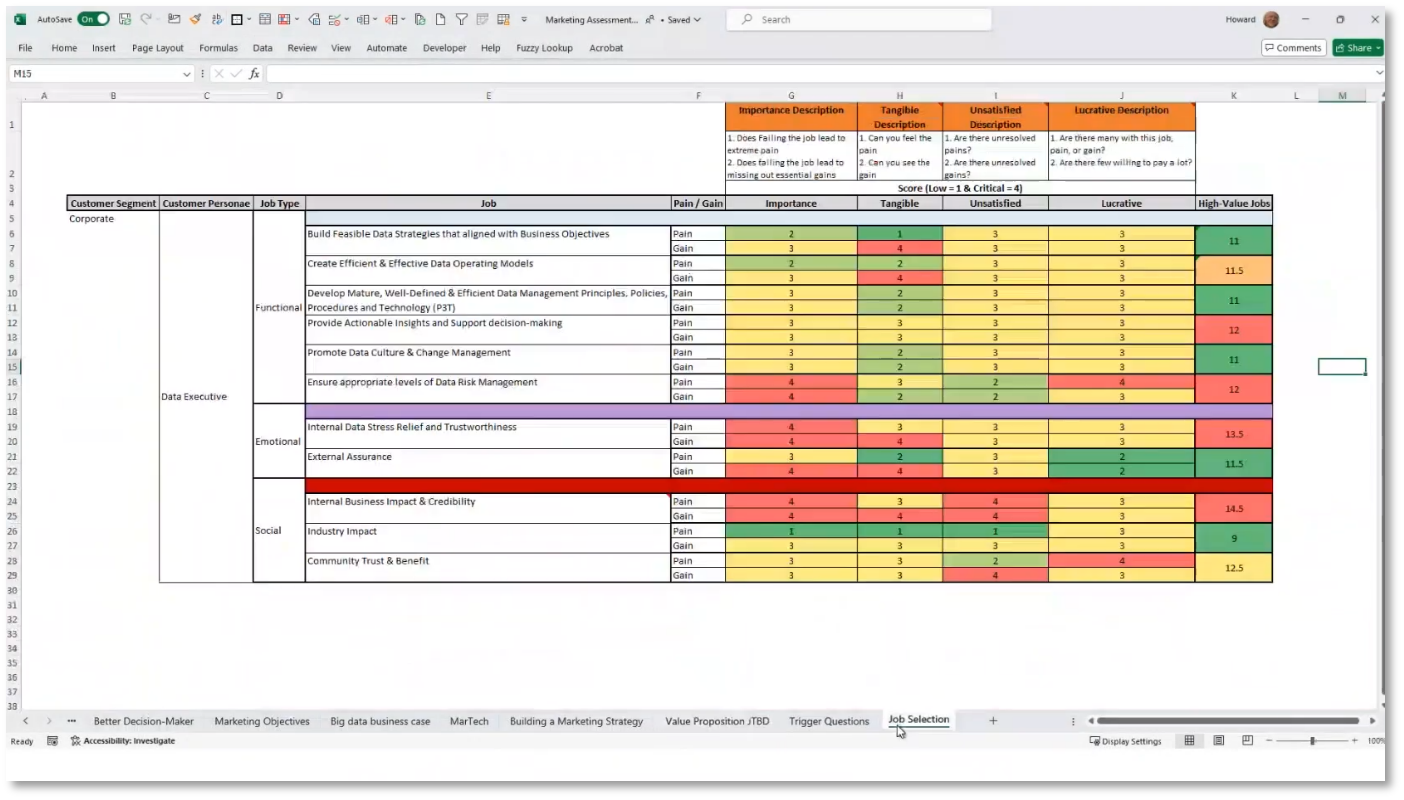
Figure 26 High-Value Job Definition & Prioritisation for CDO
Figure 27 Marketing Assessment
Importance of Understanding Customer Needs and Jobs
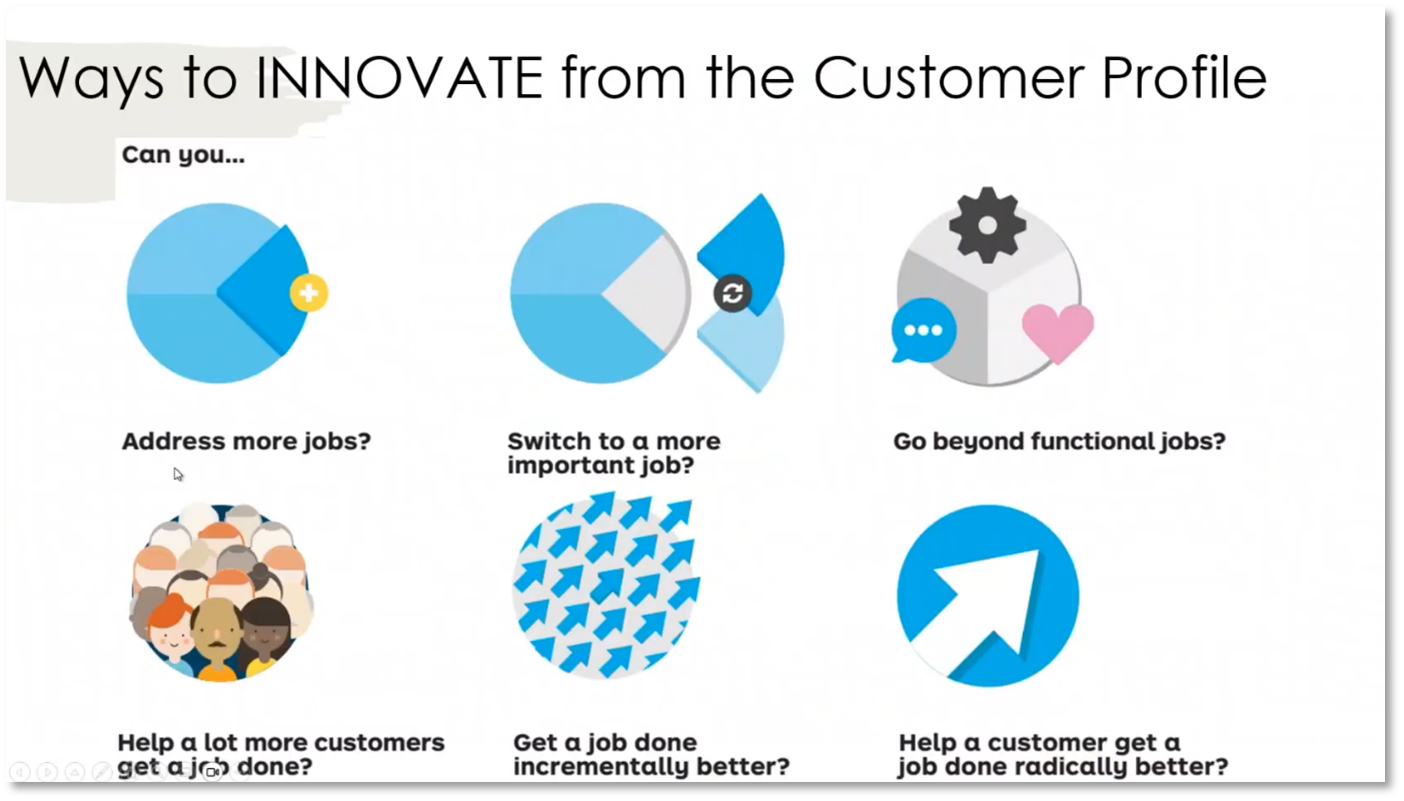
In today's business environment, understanding customers' emotional and social states is essential to gain insights into their behaviour and needs. Howard mentions a blog post by a Chief Data Officer highlighting the importance of identifying customers' pains and gains, emphasising the need to ensure that products or services are the right fit. It's crucial to engage with Chief Data Officers at their level to understand their needs and challenges, as data-related topics may not always be relatable to them. Furthermore, quick and efficient processes are necessary to conduct root cause analysis, collect data, build products, and validate them to meet business requirements. Additionally, the emphasis is on building platforms and products that effectively understand and address customer needs.
Figure 28 Ways to INNOVATE from the Customer Profile
Figure 29 Techniques to GAIN Customer Insights
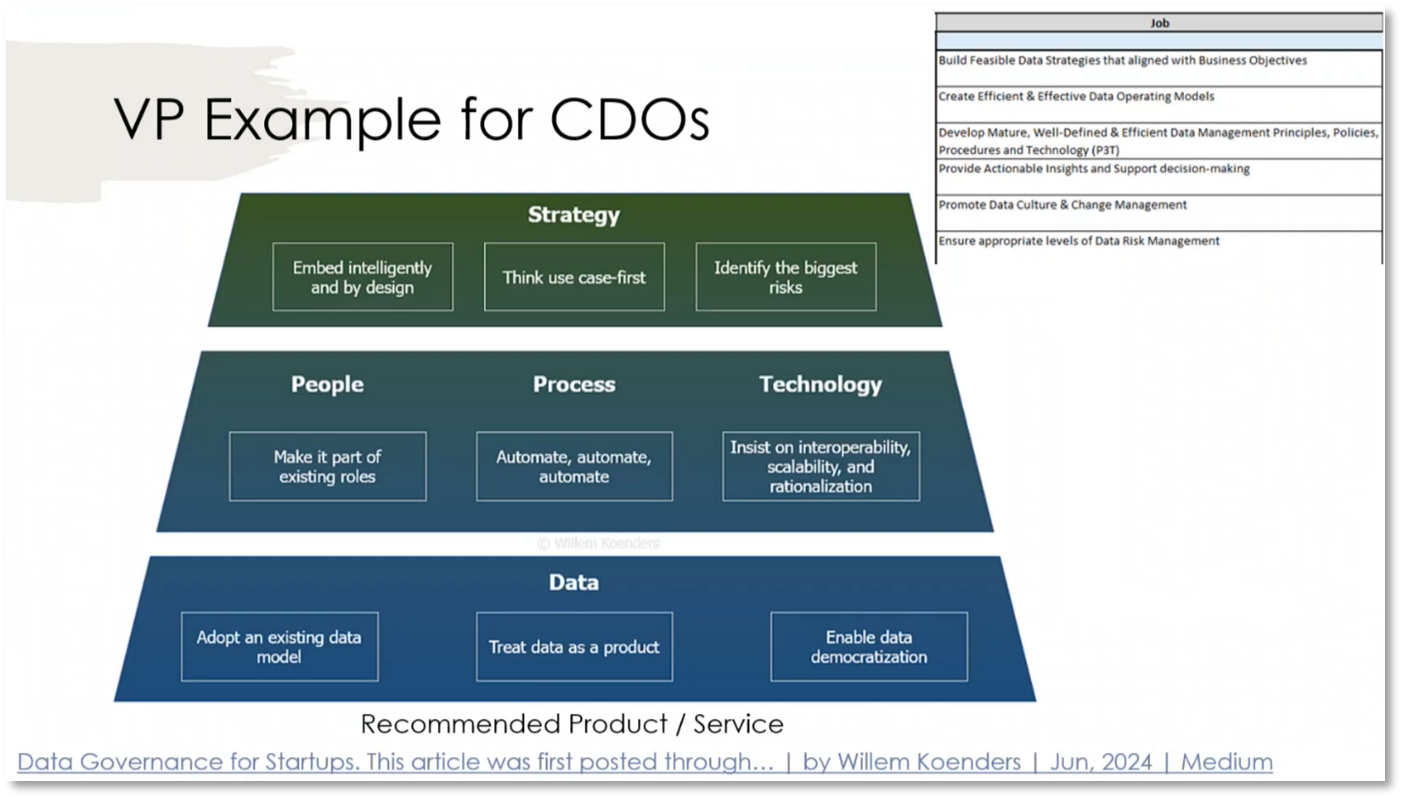
Figure 30 VP Example for CDOs - Pains and Gains Creators
Figure 31 VP Example for CDOs
Enterprise Level Problem Solving and Value Proposition
Understanding the enterprise-level problem is crucial for impacting the value proposition, which involves comprehending the jobs, priorities, pains, and gains related to the problem. Identifying and prioritising the most significant pain and gain and focusing on one job, pain, and gain can lead to delivering value incrementally and radically. Balancing the needs of group entities and internal projects is essential for adding value to the implemented products and services. Additionally, showing the value of the alignment framework for managing master and reference data is crucial for reporting and demonstrating impact to the group.
Importance of Measurement and Data Collection in Business Strategy
In business strategy, measurement and data collection are crucial for success. It is essential to continuously measure and present the progress of the business strategy, using trigger questions and a framework such as the Data Value Driven Playbook and ideation stage for data collection and alignment with business architecture. Connecting the strategy to the return on investment and identifying pain points and gains is essential. In contrast, continuous messaging and repetition of the strategy's purpose and progress are emphasised for alignment and progress.
Figure 32 Importance of Measurement and Data Collection in Business Strategy
Framework for Customer Jobs and Contexts
A structured approach to identifying customer needs involves asking trigger questions such as identifying the customer's primary goal, the steps taken to achieve it, and the various situations they may encounter. Recognising that a single individual can fulfil multiple roles in different contexts, leading to diverse needs, is crucial. This framework is useful for creating a company and defining customer services. It enables the examination of customer profiles at local, regional, and global levels to assess the scalability and applicability of services beyond the local setting. Addressing local challenges and gains makes it possible to identify scalable solutions that can be applied beyond the local context, thereby enhancing business scalability.
Importance of Entrepreneurial Mindset in Business
Gaining money in business requires a solid framework, understanding customer needs, and delivering value. An attendee recommends training employees to think like business owners. Both entrepreneurs and employees need to recognise the value they can add. Emphasising an entrepreneurial mindset is beneficial for starting and working within a company.
If you would like to join the discussion, please visit our community platform, the Data Professional Expedition.
Additionally, if you would like to be a guest speaker on a future webinar, kindly contact Debbie (social@modelwaresystems.com)
Don’t forget to join our exciting LinkedIn and Meetup data communities not to miss out!